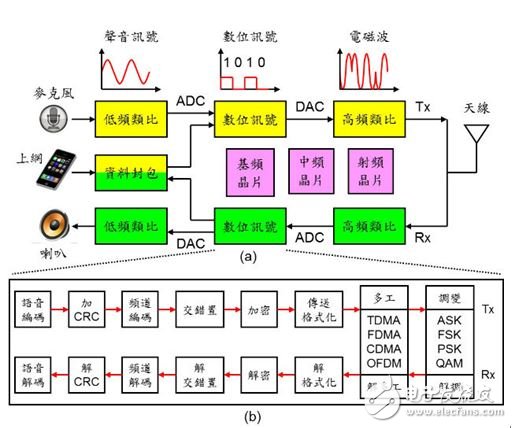
The spectrum of wireless communication is limited, the distribution is very strict, and the electromagnetic waves of the same bandwidth can only be used once. In order to solve the problem of many problems, engineers have developed a number of "modulation technology" (ModulaTIon) and "multi-tasking technology" (MulTIplex) to increase the spectrum. Efficiency, so the invention of 3G, 4G, 5G different communication technologies, then what components in our mobile phone are responsible for handling these technologies for us? Modulation technology and multitasking technology First of all, we need to understand that ModulaTIon is completely different from Multi-tasking (MulTIplex). Let's first look at how they differ. Digital Signal Modulation Technology (ASK, FSK, PSK, QAM): Transforms the simulated electromagnetic waves into different waveforms to represent two different digital signals, 0 and 1. ASK uses amplitude to represent 0 and 1, FSK uses frequency to represent 0 and 1, PSK uses phase (waveform) to represent 0 and 1, QAM uses both amplitude magnitude and phase (waveform) to represent 0 and 1. Well, the digital signals 0 and 1 that each person's cell phone antenna is going to transmit become electromagnetic waves of different waveforms. The problem is again. So many different waveforms of electromagnetic waves are thrown into the air. How to distinguish those that are yours (and What are you talking about, those are my (and I talked to)? Multitasking technology (TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, OFDM): Differentiate electromagnetic waves for different users. TDMA uses time to distinguish between yours and me. FDMA uses different frequencies to distinguish between yours and mine. CDMA uses different passwords (orthogonal spreading codes) to distinguish between yours and me. OFDM uses different positives. The subcarrier frequency is used to distinguish between yours and mine. It is worth noting that digital signal modulation technology or multi-tasking technology is performed together when digital signals (0 and 1) are operated and processed. Therefore, multi-task technology and modulation technology must be used simultaneously. Digital modulation technology (Digital modulation) The current mobile phone belongs to "digital communication", which is the voice of our speech (continuous analog signal), which is first converted into discontinuous 0 and 1 digital signals by the mobile phone, and then converted into electromagnetic waves (analog signals) through digital modulation. Carrying the digital signal), and finally transmitting it from the antenna, the principle is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1: Schematic diagram of digital communication. (Source:the Noun Project) Digital communication system architecture The architecture of the digital communication system is shown in Figure 2 (a). The user may use a smart phone to make a voice communication or access the Internet for data communication. We explain the following: Figure 2: Schematic diagram of the communication system architecture. Voice upload (talking): The sound is received by the microphone and then is a low-frequency analog signal. It is converted into a digital signal by a low-frequency analog-to-digital converter (ADC), and is compressed (Encoding) and cyclically via a "basic chip (BB)". Repeated check code (CRC), channel coding, inter-leaving, ciphering, formatting, digital signal processing such as multiplexing, modulation, etc. , as shown in Figure 2 (b). Next, it is converted into a high-frequency analog signal (electromagnetic wave) by a high-frequency digital-to-analog converter (DAC); finally, electromagnetic waves of different time, frequency, and waveform are formed by the "radio frequency chip (RF)" to be transmitted by the antenna. Voice download (listening to the phone): The antenna receives electromagnetic waves of different time, frequency and waveform, and obtains high-frequency analog signals (electromagnetic waves) after being processed by "radio frequency chip (RF)", and then passes through a high-frequency analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Convert to digital signal. Next, demodulation, de-multiplexing, de- formatting, de-ciphering, and de-interlacing are performed via "baseband chip (BB)". -inter-leaving), channel decoding, decyclic repeat check code (CRC), data decompression (Decoding) and other digital signal processing, and finally converted to low frequency simulation via low frequency digital-to-analog converter (DAC) The signal (sound) is played back by the headphones. Data communication (online): Basically, data communication is digital signal regardless of uploading or downloading, so it can be directly processed into the baseband chip (BB). Other processes are similar to voice communication, and will not be repeated here. Note: The principle of communication is a lot of mathematics. Since the mobile phone is something we use every day, most people are curious about the feeling of communication and want to know more, but often go into the first class of the classroom to see It is a lot of complicated numbers: Fourier Transform, Laplace Transform, Discrete, and immediately retreat. In order to simplify the complexity, it is easy for everyone to understand. The above is for digital communication systems. The introduction is just a gesture, and there will be a gap with the actual situation. It is recommended that those who are interested in further understanding can base on the above concepts to further understand the technical details. Communication related integrated circuit: baseband chip, intermediate frequency chip, radio frequency chip Baseband (BB): A digital integrated circuit used for compression/decompression of digital signals, channel encoding/decoding, interleaving/de-interlacing, encryption/decryption, formatting/deformatting, and more Task/de-task, modulation/demodulation, and management of communication protocols, control input and output interfaces, etc., have been integrated into a "system on a chip (SoC)", a famous mobile phone. Baseband chip suppliers include: Qualcomm, Broadcom, Marvell, MediaTek and more. Intermediate Frequency (IF): Due to the high frequency of communication electromagnetic waves, it is difficult to increase the frequency of the signal directly to the frequency of the electromagnetic wave (GHz) from the digital signal. Therefore, the signal frequency can be higher than the high frequency. The electromagnetic wave is still low in the "intermediate frequency". The early communication system has an IF chip. Later, due to the advancement of "Direct Conversion" technology, the signal sensitivity and noise can be overcome. The RF can be directly reduced to the fundamental frequency. The IF chip can save space and reduce costs, achieving the goal of Zero IF (ZIF). Radio Frequency (RF): Also known as Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit (RFIC), it is a general term for all chips that process high-frequency electromagnetic waves. It usually includes: Transceiver, Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), Power Amplifier. (PA), bandpass filter (BPF), synthesizer, mixer, etc., typically MEMSFETs made of gallium arsenide wafers, HEMT components, or BiCMOS components fabricated from silicon germanium wafers, Or a CMOS component made of silicon wafers. Currently, a power amplifier made of gallium nitride (GaN) may be a plurality of integrated circuits (ICs), and some may be integrated into a single system-on-chip (SoC). 57 Series Centronic Connectors Current Rating:5A 57 Series Centronic Connectors ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkwire.com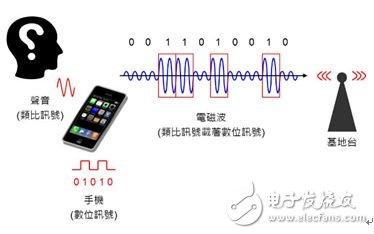
Dielectric Withstanding Voltage:1000V for one minute
Insulation Resistance:1000MΩ Min.(at 500V DC)
Contact Resistance:35mΩ Max.
Temperature:-55°C to +105°C