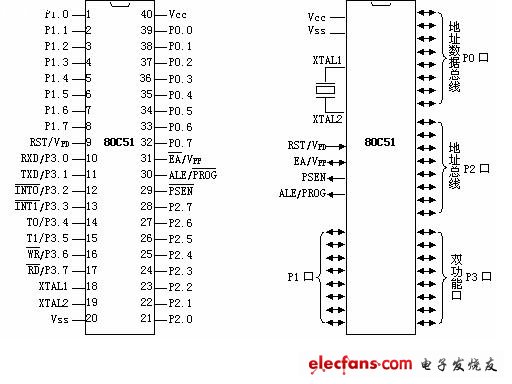
Lead: MCU is really difficult for beginners to understand, many students who have studied SCM or electronic enthusiasts, even when they graduated, they still have nothing. Based on this, the electronic enthusiast network will integrate the "single-chip knowledge of the key points of the single-chip", divided into four series, to readers, so stay tuned! This series also has collection and reference value for electronic engineers in the industry. A list of key knowledge points of the microcontroller: Series one Series two Series three Series four 1: Microcontroller brief What is a single-chip computer? A computer that can work has several parts: CPU (for operation, control), RAM (data storage), ROM (program storage), input/output devices (for example: serial port, parallel Output port, etc.). These parts are divided into a number of chips on a personal computer and a printed circuit board called a motherboard is mounted. In the MCU, these parts are all implemented in an integrated circuit chip, so it is called a single-chip (single-chip) machine, and some MCUs integrate other parts like the above. A/D, D/A, etc. The MCU is a control chip, a tiny computer, plus crystal oscillator, memory, address latch, logic gate, seven-segment decoder (display), buttons (similar to the keyboard), expansion chip, interface, etc. system. 2: Microcontroller pin introduction The 40 pins of a microcontroller can be roughly divided into four categories: power, clock, control, and I/O pins. 1. Power supply: (1) VCC - chip power supply, connected to +5V; (2) VSS - ground terminal; 2. Clock: XTAL1, XTAL2 - Inverting input and output of crystal oscillator circuit. 3. Control line: There are 4 control lines. (1) ALE/PROG: Address Latch Enable / On-chip EPROM Programming Pulse 1 ALE function: used to latch the low 8-bit address sent by P0 port 2 PROG function: Chip with EPROM on chip. During EPROM programming, this pin inputs programming pulse. (2) PSEN: External ROM read strobe signal. (3) RST/VPD: Reset/standby power. 1 RST (Reset) function: reset signal input. 2 VPD function: Connect the backup power supply when Vcc is powered off. (4) EA/Vpp: internal and external ROM selection / on-chip EPROM programming power supply. 1 EA function: internal and external ROM selection. 2 Vpp function: Chip with EPROM on chip, during programming of EPROM, apply programming power supply Vpp. Portable Dry Herb Vaporizers,Handheld Liquid Vaporiser,Gold Evaporator With Titanium Enclosure,Portable Dry Herb Vaporizer END GAME LABS , https://www.eglvape.com
![]() 1: Microcontroller brief
1: Microcontroller brief ![]() 2: Microcontroller pin introduction
2: Microcontroller pin introduction ![]() 3: MCU memory structure
3: MCU memory structure ![]() 4: The first microcontroller small program
4: The first microcontroller small program ![]() 5: Analysis of single-chip delay program
5: Analysis of single-chip delay program ![]() 6: Single-chip parallel port structure
6: Single-chip parallel port structure ![]() 7: Special function register of the microcontroller
7: Special function register of the microcontroller ![]() 8: Single-chip addressing mode and command system
8: Single-chip addressing mode and command system ![]() 9: MCU data transfer instructions
9: MCU data transfer instructions ![]() 10: MCU data transfer instructions
10: MCU data transfer instructions ![]() 11: MCU arithmetic operation instruction
11: MCU arithmetic operation instruction ![]() 12: Single-chip logic operation instruction
12: Single-chip logic operation instruction ![]() 13: Single-chip logic and or XOR instruction
13: Single-chip logic and or XOR instruction ![]() 14: MCU conditional transfer instruction
14: MCU conditional transfer instruction ![]() 15: MCU bit operation instruction
15: MCU bit operation instruction ![]() 16: MCU timer and counter
16: MCU timer and counter ![]() 17: The way of the microcontroller timer / counter
17: The way of the microcontroller timer / counter ![]() 18: Interrupt system of single chip microcomputer
18: Interrupt system of single chip microcomputer ![]() 19: MCU timer, interrupt test
19: MCU timer, interrupt test ![]() 20: Microcontroller timer/counter experiment
20: Microcontroller timer/counter experiment ![]() 21: Introduction to the serial port of the MCU
21: Introduction to the serial port of the MCU ![]() 22: Design of serial port communication program of single chip microcomputer
22: Design of serial port communication program of single chip microcomputer ![]() 23: LED digital tube static display interface and editing
23: LED digital tube static display interface and editing ![]() 24: Dynamic scan display interface circuit and program
24: Dynamic scan display interface circuit and program ![]() 25: Microcontroller keyboard interface programming
25: Microcontroller keyboard interface programming ![]() 26: Single-chip matrix keyboard interface technology and
26: Single-chip matrix keyboard interface technology and ![]() 27: Some basic concepts about microcontroller
27: Some basic concepts about microcontroller ![]() 28: Actual case practice - MCU music program design
28: Actual case practice - MCU music program design