The frequency divider is to distinguish the sound signals of different frequency bands, respectively give amplification, and then send them to the speakers of the corresponding frequency bands for playback. In high quality sound reproduction, electronic crossover processing is required. The crossover is a kind of circuit device in the speaker, which separates the input analog audio signal into different parts such as treble, midrange and bass, and then respectively sends them into the corresponding high, medium and low woofer units for playback. The reason for this is that no single speaker can perfectly reproduce the full frequency of the sound. The crossover is the "brain" in the speaker, which is very important for the sound quality. The music signal output by the power amplifier must be processed by the filter wave component in the frequency divider to allow the signals of specific frequencies of each unit to pass. It is necessary to scientifically design, rationally and rigorously design the frequency divider of the speaker to effectively modify the different characteristics of the speaker unit, optimize the combination, so that each unit can develop its strengths and avoid weaknesses, and exert its potential as much as possible to make the frequency response of each frequency band change. Smooth, accurate phase of the sound image, in order to make the music played by high, medium and low sounds clear, co-ordinated, clear, comfortable, wide and natural sound quality. In a speaker system, people refer to the box, frequency dividing circuit, and speaker unit as the three major parts of the speaker system, and the frequency divider is the "brain" in the speaker. The frequency dividing circuit can restore the speaker system with high quality. Electroacoustic signals play an extremely important role. Especially in the middle and high frequency parts, the role played by the frequency dividing circuit is more obvious. In general, the frequency divider can be defined as: separating the input electrical signal into two separate signals, and making the bandwidth of each signal smaller than the bandwidth of the original signal, such as one or more pairs of filters The device constructed is called a frequency divider. It can also be called a "frequency allocation network." The frequency divider is usually composed of a high pass (low cut) filter (abbreviated as HPF) and a low pass (high cut) filter (abbreviated as LPF). A filter is a frequency selective device that blocks other frequencies from passing through the selected frequency. The filter usually has the following three parameters: cutoff frequency, network type, and slope. The cutoff frequency is the frequency at which the filter's response drops below a certain level below its maximum level, typically 0.707 or 0.5 times the maximum level, or a frequency that drops 3dB or 6dB. In general, the divider consists of three basic parameters: the crossover point, the way and the step. The meaning of each parameter is described in detail below. The crossover point refers to the demarcation point between the divider high pass, band pass and low pass filter, expressed in common frequency, in Hertz. There are only one crossover point for the high and low frequency two-way speakers. The high, medium and low three-way speakers have two crossover points. The crossover point should be determined according to the frequency characteristics and power distribution of the speaker units or speakers in each frequency band. The crossover point is usually defined as the frequency at which the responses of two frequency dividers (generally consisting of one LPF and one HPF) cross each other, possibly the crossover of the electrical characteristics of two electronic frequency dividers (slave or active). Point, or the crossover point on the two acoustic filters. Any speaker unit is essentially a filter, each with its own high-pass and low-pass filters, as well as inherent cutoff frequency, slope, and network type. The overall acoustic crossover point of a system depends on the mathematical combination of the electronic filter and the frequency response of the horn unit in this system. When an electronic filter is added to an acoustic filter system, their frequency response will be superimposed to form a brand new Response curve. The difference in sound level/sensitivity between two different units, and the phase lag of the high frequency device are all obvious. The high frequency portion is likely to be fixed to the horn of a long throat, thus creating a delay relative to the low frequency loudspeaker. In order to better reproduce the signal, the newly developed frequency divider is required to smooth the frequency response curve. Selection principle The choice of crossover points is more flexible, but there are several dominant theories in general. 1, the frequency characteristics of the high and low speakers, the crossover point should choose the more appropriate between the two, so that the full band is smooth. 2, high-woofer speaker for different frequency sound performance, some units are suitable, and some are not suitable. 3, the quality of the tweeter, especially when the crossover point is low, the tone and power carrying capacity of the tweeter is very high. Method of choosing 1. Consider the medium-low cell directivity practical boundary frequency f=345/d (d=unit diaphragm effective diameter). Usually, the boundary frequency of the 8" unit is 2k, the boundary frequency of the 6.5" unit is 2.7k, the 5" unit is 3.4k, and the 4" unit is 4.3k. That is to say, using the above unit, the frequency division point cannot be greater than the practical boundary frequency corresponding to each unit. 2. Considering the resonant frequency of the tweeter, the crossover point should be greater than three times the resonant frequency. That is to say, from the perspective of the tweeter, usually the crossover point should be greater than 2.5k. 3. Consider the high-end response Fh of the mid-woofer unit. Usually, the crossover point should not be greater than 1/2Fh. In fact, the above conditions of the two-way speaker are difficult to obtain at the same time. At this time, the designer should have a better compromise among the three. However, it must be emphasized that the first condition, the practical boundary frequency, should be given priority. 4. In the case of three-way, the farther the two crossover points should be separated (should be above three octaves), the better the system response will be. Otherwise, complex interference radiation will occur. 5, the crossover point of the bass and midrange should consider the problem of vocal image positioning. The playback of the vocals should be undertaken by the midrange unit as much as possible to avoid excessive changes in the vocal positioning sound of the vocals. This is often overlooked by designers. Usually this crossover point should be 200-300HZ. Guangzhou Chengwen Photoelectric Technology co.,ltd , http://www.cwledpanel.com
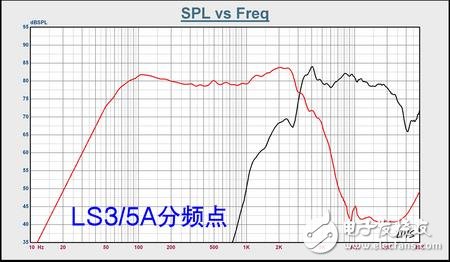
What is a crossover?