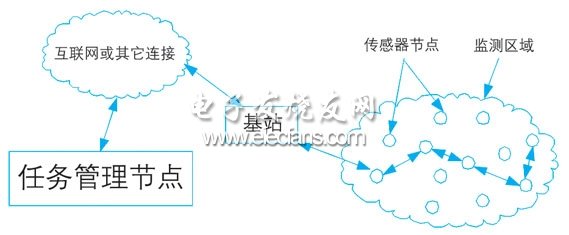
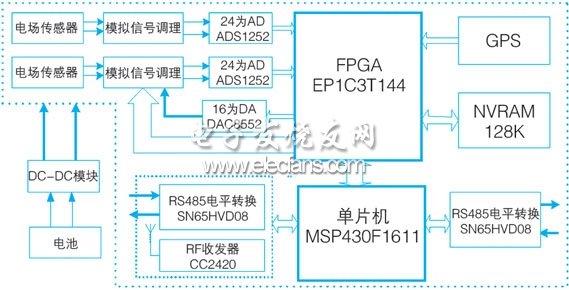
1 Introduction A wireless sensor network (wireless sensor network, wsn) is an intelligent network monitoring system that consists of a large number of tiny nodes that integrate sensors, data processing units, and short-range wireless communication modules, and can automatically complete specified tasks according to the environment. WSN does not require fixed network support, and has the characteristics of rapid deployment and strong resistance to destruction. It can be widely used in military reconnaissance, environmental monitoring, medical monitoring, agricultural breeding and other commercial fields, as well as special fields such as space exploration and disaster relief. The distributed electromagnetic detection system achieves the purpose of exploration by detecting the electrical difference of the underground target body and analyzing the abnormal distribution law. Due to the harsh working environment in the field, blocked gullies and rivers, and complicated terrain, it is difficult for exploration personnel to access or overtake some areas. The use of traditional wired connections not only greatly increases the workload, but also makes some areas unable to explore because they cannot be wired. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to construct a distributed electromagnetic detection system by means of wireless sensor networks. 2 Wireless sensor network analysis 2.1 Wireless sensor network hardware composition The hardware design and networking of sensor networks are closely related to the application field. A typical wireless sensor network is mainly composed of three parts in hardware, namely a sensor node, a base station (also called a terminal node, an aggregation node), and a task management platform. Among them, sensor nodes are the main components of the network. They have the dual functions of network terminals and routers. In addition to local information collection and simple data processing, they also need to store, manage, and integrate data forwarded by other nodes. They are widely distributed in data monitoring. Area, the physical form of the monitored signal determines the type of sensor node; the base station is used to exchange data between the two communication networks, realize the communication protocol conversion between the two protocol stacks, manage the node, and forward the collected data to On the external network. The task management platform detects and manages the entire network and processes data, usually a PC or a handheld device running management software. The typical wireless sensor network composition structure is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Typical wireless sensor network composition structure 2.2 Network protocol The wireless sensor network communication protocol stack mainly includes a physical layer, a data link layer, a network layer, a transmission layer, and an application layer. Although many researchers have put forward some solutions for each layer of the sensor network, but generally have not yet formed a widely accepted standard. ieee802.15.4 standard is a communication standard for low-speed wireless personal area network (pan), with low power consumption and low cost as the main goals of the design, aiming to provide low-speed networking between different devices within the personal or family range Uniform standards. Due to the similarities between the network characteristics of IEEE802.15.4 and wireless sensor networks, many research institutions regard it as the communication standard for wireless sensor networks [5]. The zigbee protocol is a technical standard related to networking, security and application software developed by the zigbee enterprise alliance based on the 802.15.4 wireless standard. It has the following relationship with 802.15.4: (1) Zigbee fully and fully utilizes the advantages of the powerful physical characteristics defined by ieee802.15.4; (2) Zigbee added logical network and application software; (3) zigbee is based on ieee802.15.4 radio frequency standard, and at the same time, zigbee alliance works closely with ieee to ensure an integrated and complete market solution; (4) The 802.15.4 working group is mainly responsible for formulating the physical layer (phy) and media access control (mac) layer standards, and zigbee is responsible for the development of the network layer and application layer. 2.3 Network layer routing protocol The protocol is the soul of the wireless sensor network. Without the support of other network devices, it directly determines the network architecture. From the perspective of the network layer, routing protocols can be divided into two structural types [3]: flat and hierarchical. In the planar routing protocol, all sensor nodes have equal status. The protocol formulation is relatively simple and belongs to the peer-to-peer network structure. There is no bottleneck in the network, and the work is reliable and relatively robust. However, this protocol has poor scalability, and each node needs to know the route to all other nodes, and maintaining these dynamically changing routing information requires a lot of control messages. In the hierarchical routing protocol, the network is divided into cluster heads and multiple cluster members in units of clusters, and the cluster head nodes are responsible for forwarding data between clusters. The cluster head can be specified in advance, or it can be automatically elected by the node using an algorithm. The advantages of the hierarchical structure are: the function of the cluster members is relatively simple, there is no need to maintain complex routing information, and the amount of routing control information in the network is reduced, so it has good scalability; because the cluster head node can be elected at any time , The hierarchical structure is also very robust. However, the disadvantage of the hierarchical structure is also obvious: maintaining the hierarchical structure requires nodes to execute the cluster head election algorithm, and the cluster head node may become a bottleneck for network transmission. Therefore, when designing a network routing protocol, if the scale of the network is small, a simple flat structure can be adopted; and when the scale of the network increases, the hierarchical structure is applied. 3 Design of distributed electromagnetic detection system 3.1 Hardware design This system is mainly composed of three parts: sub-station, base station and management platform. The substation is an embedded microprocessor system used to complete various electrical measurement functions, such as resistivity, excited polarization potential ip (time domain and frequency domain), controllable source audio magnetotelluric csamt (scalar, vector , Tensor) and other measurements, the measured parameters are mainly electric and magnetic fields. The sub-station uses msp430f1611 as a microprocessor. It is a high-performance low-power 16-bit single-chip microcomputer with rich storage resources and interfaces, which is easy to integrate peripheral devices. Arranged at each measuring point in the detection area. Using high-performance ieee802.15.4 / zigbee compatible radio frequency chip cc2420 as the wireless transceiver module, can make the equipment and 802.15.4 standard equipment to achieve interconnection and interoperability, can work in the 2.4g unlicensed band, supports 16 maximum transmission rate of 250kbps Channel; also adopts dsss technology, has strong anti-interference; built-in transceiver RF switch, hardware mac encryption (aes-128), supports digital rssi / lqi, the interface with the processor is relatively simple, and is at the leading level in the industry . The overall design of the substation is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2 Block diagram of the overall design of the substation The base station realizes the exchange of network data, controls the data collection and transmission of the sub-station, and sends the data to the management platform. The base station adopts the PC104 embedded platform design. The platform is compatible with the IBM PC, with rich on-chip resources and flexible and extensible. The small size is very suitable for the application of embedded systems. It is fast and accurate in data acquisition, suitable for the operation of various software development environments, and meets the design requirements of this system. The overall design of the base station is shown in Figure 3. Figure 3 Block diagram of the overall design of the base station In the field exploration operation, a laptop computer can be used as a host computer to function as a task management platform. The host computer can build, manage and detect the network by sending command information to the base station, control the operation of the system, and conduct the collected data Real-time processing. Considering that the network construction of the distributed electromagnetic detection system is not complicated, the measurement network can adopt a star-shaped planar structure, but it must ensure reliability; in order to ensure the transmission of remote data, the problem of multi-hop routing must be considered. This is a routing protocol design. A key element of time. Guangzhou Bolei Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.nzpal.com