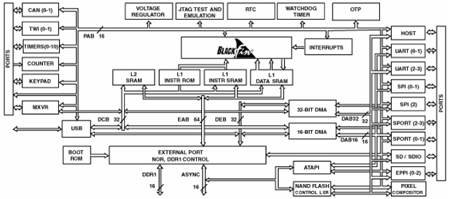
Manufacturers in the automotive industry are facing challenges. Consumers always expect their cars to have the latest audio and multimedia systems, as well as interfaces to portable devices such as MP3 players. Since the consumer electronics industry is growing faster than the traditional automotive industry, automakers and Tier 1 suppliers must keep up with the times. This article refers to the address: http:// Because media formats and communication standards are constantly changing, the flexibility of software is very important for automotive applications. This means that general purpose processors are usually a good choice because they allow for simple low cost and high efficiency changes to accommodate automotive multimedia systems. Manufacturers want their cars to stand out from the competition, and in-vehicle multimedia systems can provide them with valuable solutions. This article will cover the multimedia solutions in Audi's latest A5 car and discuss the standards and issues related to automotive multimedia. The Audi A5 in the latest Audi car system is a typical example of a modern car multimedia system. It integrates four Blackfin processors to provide digital RF transceivers (Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB)), MP3-compatible 6-disc CD autochangers and Audi's music interface, which allows users to interact with Apple The iPod media player is connected and can be used with multi-function controls mounted on the steering wheel. Its optional accessory is a surround sound amplifier from Bang & Olufsen (B&O), which is based on In the SHARC processor, the filter algorithm can be implemented to adapt the audio signal to the acoustic environment inside the car. Automotive bus standards and other challenges From an embedded system perspective, one of the main differences between cars and other applications is the bus standard used. Typically, automotive communications use a Controller Area Network (CAN) bus or a Media Oriented System Transport (MOST) bus. The CAN bus is mainly used as a control interface; its bandwidth is about 1 Mbit/s, so it is not suitable for multimedia data transmission. The MOST bus is used to transmit multimedia data in a digital format (original PCM data) with a bandwidth of up to 25 Mbit/s. Software is often used to implement the required MOST and CAN network services, using real-time operating systems (RTOS) to ensure real-time requirements are met. Multimedia systems must support standard communication protocols such as the USB OTG standard, the SDIO standard, and the Bluetooth standard. It must also support popular devices that meet proprietary protocol requirements, such as the Apple iPod player and Microsoft's Zune player. USB memory and many different multimedia devices can be connected to the system as a USB host, and a personal computer (PC) can also be connected to the system as a USB device. Typically, USB and SDIO standard software devices and their respective file systems are an integral part of the operating system. Multimedia gateway and car audio body To support automotive multimedia applications, the main task of embedded systems (referred to as "multimedia gateways") is to adapt and translate proprietary and standard communication protocols, such as the Bluetooth protocol, the USB protocol, and the decoding of digital audio formats. The multimedia gateway uses a custom programmable processor that is open to software upgrades, thus speeding up development and enabling automakers to respond appropriately to rapid changes in the consumer electronics market. To date, multimedia gateways have been the only solution for cars. A new generation of car audio bodies (also known as head units) combines the human-machine interface (HMI) integrated in the dashboard with the multimedia capabilities of the gateway. The car audio body may also integrate other functions such as communication and navigation. It requires far more integration than the gateway, thus extending development time but reducing costs and increasing efficiency. The software and hardware requirements of the car audio body are higher than the multimedia gateway, because its processor must implement the common functions of the HMI and the gateway, and if necessary, support the digital radio frequency transceiver standard. The HMI is typically implemented by a separate processor that has an interface to the display directly in the car and may include speech recognition and text-to-speech output. Powerful processors such as the Blackfin BF549 can perform the required functions and provide an extensible platform. In the latest Audi A5, the Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI) of the Black fin ADSP-BF539 processor with a clock speed of up to 533MHz is used to control the multimedia interface (MMI) graphics display of the "symphony" and "concert" RF transceivers. . MMI was developed using advanced software tools designed to graphical user interfaces that allow users to prototype HMI user interfaces and emulate other customized versions. Figure 1 Multimedia gateway provides isolation between audio devices and automotive electronics Problems under the dashboard The Blackfin processor provides the Audi with the performance it needs and the flexibility of connectivity and field upgrades. Other processor architectures are also considered, but the Blackfin processor is chosen because it provides the performance, scalability, and scalability required for audio processing, DAB processing, and MMI control in Audi's in-car entertainment information system. It also supports infrastructure for fast, low-risk development. ADI's high-end audio system experience also helps influence decision making because it provides third-party intellectual property (IP) protection for a variety of specific industries. The ADSP-BF532 processor provides optional digital audio broadcasting (DAB) functionality. Audi's Symphony and Concert DAB RF Transceiver is a software-defined radio (SDR) solution that allows Audi to implement new RF transceiver protocols using the latest software. Future upgrades only require downloading the software flash of the new IP into the programmable hardware of the processor. . Another Blackfin processor connected to the MOST bus can drive an MP3 compatible 6-disc CD autochanger. The processor implements MOST network services using software. Another Blackfin processor can drive the music interface of the Audi A5, which integrates a portable media player such as the Apple iPod, which can be displayed on the dashboard display or controlled by the steering wheel. This interface can also duplicate audio displays on the iPod player display, such as music titles. For the above applications, the 400MHz processor has a suitable price/performance ratio. The processor is able to perform control and signal processing, which also means that it must complete audio processing and management of external devices. The internal structure of the Blackfin multimedia processor is shown in Figure 2. Connectivity is provided through a number of serial interfaces (3 SPI, 4 UARTs, 4 SPORTs, and 2 TWIs) as well as a USB-OTG interface, an ATAPI interface, and an SDIO interface. In addition, it has three parallel interfaces for driving the display, digital camera and another processor for navigation services. Two CAN interfaces and one MXVR interface provide a connection between the processor and the vehicle's internal bus. Figure 2 Block diagram of the Blackfin BF549 processor Automotive multimedia applications require powerful processors. The BF549 Blackfin processor has a 32-bit architecture and a fast dual A double data rate (DDR) memory interface that can process video data with a resolution of WVGA (800 x 480). This means it can control demanding situations, such as processing synchronized audio files and simultaneously completing MOST network services and Bluetooth communications. Developers of all design teams in the Audi A5 project use Analog Devices' VisualDSP++ Integrated Development and Debug Environment (IDDE). The environment includes native C/C++ compilers, advanced drawing tools, statistical monitors, and the VisualDSP++ kernel (VDK), which allows code to be written in a structured and simple way. DRM problem Any audio purchased may contain files protected by Digital Rights Management (DRM). In order to be able to replay digital audio, the decoder must support the corresponding DRM format. Decoding Microsoft's DRM (PlayforSure) requires DRM authentication, which must be permanently stored on the gateway. Storage DRM authentication raises a special issue because it is important to properly protect DRM from unauthorized access. The Blackfin processor is protected according to the security concepts identified by software and hardware. The specially developed Lockbox technology is used to handle digital rights management. DRM authentication is stored in dedicated One Time Programmable (OTP) memory. The OTP can only be accessed by an authenticated application during system startup. In addition, the application can be partially or fully encoded to prevent any secret theft or illegal copying. The role of wireless communication in the future In the future, wireless data transmission will play a special role, because this connection is very suitable for transmitting audio and video data between portable devices and cars. In addition to the hands-free communication application (Hands Free Application Specification, HFP for short), the Bluetooth protocol also supports a variety of new specifications. One of these latest specifications is the A2DP specification, which allows users to regenerate audio files in their phones through the car's audio system. A2DP is an abbreviation for Advanced Audio Transmission Specification that uses a wireless Bluetooth connection to transmit compressed audio data such as MP3 and AAC. Table 1: Audio Editing Decoder The AVRCP specification extends the A2DP specification. This specification allows users to replay music from their phones. It usually includes start, stop, next track, previous track, and quick playback of the song. The specification also supports raw data, and in the future it may also display a title on the display of the RF transceiver, allowing the user to select a favorite song or play a list of songs through the central user interface. The DUN configuration file (Dial-Up Networking Profile) is another important configuration file. This file provides connectivity options for base stations and mobile phones and allows users to access the Internet directly. Its data transfer speed depends on the transmission standard, which means it can provide many new telematics functions. In addition to pure communication support, the multimedia gateway can handle the simultaneous encoding of several digital format audio files, which can use digital rights management (DRM). In the future, two to three separate audio zones in the car can be supported to meet the requirements of all passengers. The table below summarizes the most important audio codecs. Outlook After the audio application, the video application will be launched, which will increase the hardware requirements. The data transfer rate required for audio is about a few hundred Kbit/s, and the video data transfer rate rises to several Mbit/s. In this case, the video data must be distributed to one or several video sources within the car, such as a DVD or hard drive. In the future, the MOST standard (MOST150) will still be used, which can transmit data rates up to 150 Mbit/s. When transmitting video data, the Bluetooth standard is also close to the transmission limit because its maximum data rate of 2 Mbit/s can only be used to replay small video files. For short-range wireless networks, the Bluetooth standard will be replaced by the new Wireless USB standard, which is capable of transmitting data rates up to 480 Mbit/s. In the future, the issue of how cars connect to the Internet remains to be resolved, and the trend of increasing data transmission rates will not end. Busbar Copper,Busbar Insulator,Tin Plated Copper Busbar,Lithium Battery Busbar Dongguan Andu Electronic Co., Ltd. , https://www.idofuse.com