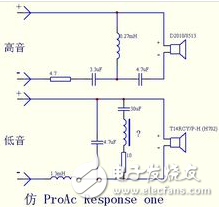
The analog crossover is a circuit device in the speaker that separates the input analog audio signal into different parts such as treble, midrange, and bass, and then sends them to the corresponding high, medium, and woofer units for playback. The reason for this is that no single speaker can perfectly reproduce the full frequency of the sound. From the circuit structure point of view, the frequency divider is essentially an LC filter network composed of a capacitor and an inductor coil. The high-pitched channel is a high-pass filter, which only allows high-frequency signals to pass through and blocks low-frequency signals; the bass channel is just the opposite, it only allows The bass passes through to block the high-frequency signal; the mid-range channel is a band-pass filter, except that the frequency between the two low-high and high-frequency points can pass, and both the high-frequency component and the low-frequency component will be blocked. In the actual crossover, sometimes in order to balance the sensitivity difference between the high and low woofer units, attenuating resistors are added; in addition, some frequency dividers also include an impedance compensation network composed of resistors and capacitors. Make the impedance curve of the speaker more flat to facilitate the amplifier drive. Divider schematic Located behind the power amplifier, set in the speaker, through the LC filter network, the power audio signal output by the power amplifier is divided into bass, midrange and treble, respectively, to their respective speakers. The connection is simple and convenient to use, but the power consumption, the audio valley point, the cross distortion, the direct relationship between the parameters and the speaker impedance, and the impedance of the speaker is a function of the frequency, which deviates greatly from the nominal value, so the error Also larger, not conducive to adjustment. The device that divides the audio weak signal is located in front of the power amplifier. After dividing the frequency, each independent audio amplifier is used to amplify each audio frequency band signal and then sent to the corresponding speaker unit. Due to the small current, it can be realized with a smaller power electronic active filter, which is easier to adjust, reduce power loss, and interference between speaker units. The signal loss is small and the sound quality is good. However, this method uses an independent power amplifier for each path, which has high cost and complicated circuit structure, and is applied to a professional sound reinforcement system.
Differential pressure sensor (DPS) is a sensor used to measure the difference between two pressures. It is usually used to measure the pressure difference between the front and rear ends of a certain equipment or component.
Looseness often occurs during installation. The transmitter is connected with the three valve manifold. The bolts should be tightened diagonally. Generally, they cannot be locked at one time. The sealing ring should be densified during the installation of the three valve manifold.
Differential Pressure Sensor,Differential Pressure Transmitter Sensor,Differential Air Pressure Sensor,Adjustable Differential Pressure Sensor Taizhou Jiabo Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.taizhoujbcbyq.com