Mid range speaker:
Speakers with working frequency response range from 500~5000Hz are called mid range speakers.
FAQ
Q1. What is the MOQ? Mid Range Speaker,Mid Bass Speakers,Mid Range Car Speakers,Mid Bass Car Speakers Shenzhen Xuanda Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.xdecspeaker.com
MAX6902 pin configuration  Overview This application note demonstrates the interface between the MAX6902 real-time clock and the 8051 microcontroller, and provides routines for basic interface programs. The microcontroller used in this article is DS2250, and the software is written in C language. Working principle The program controls the SPI bus through the four general-purpose ports of the microcontroller. The microcontroller sends a control / address instruction to the MAX6902 to start data transmission. Subsequently, the microcontroller sends other data to the MAX6902 or provides SCLK, according to the command word. Section to send or receive data.
Overview This application note demonstrates the interface between the MAX6902 real-time clock and the 8051 microcontroller, and provides routines for basic interface programs. The microcontroller used in this article is DS2250, and the software is written in C language. Working principle The program controls the SPI bus through the four general-purpose ports of the microcontroller. The microcontroller sends a control / address instruction to the MAX6902 to start data transmission. Subsequently, the microcontroller sends other data to the MAX6902 or provides SCLK, according to the command word. Section to send or receive data.
The circuit schematic is shown in Figure 1, and the software is shown in Figure 2. 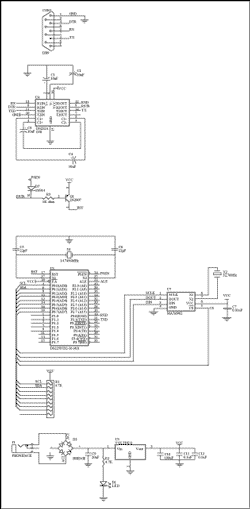
Figure 1. Schematic of daughter card (PDF download)
Figure 2. Code list / ******************************************** ******************************* / / * DEMO6902.c This program is for example only and is not supported by * / / * Dallas Semiconductor Maxim * / / ****************************************** ********************************* / #include / * Prototypes for I / O funcTIons * / #include / * Register declaraTIons for DS5000 * / / ***************************** Defines ************* ******************* / sbit CS = P0 ^ 0; sbit SCLK = P0 ^ 1; sbit DIN = P0 ^ 2; sbit DOUT = P0 ^ 3; / * ********************** FuncTIon Prototypes ************************** / void writebyte (); void iniTIalize (); void disp_clk_regs (); void burstramread (); void burstramwrt (); / *********************** ** Global Variables *************************** / uchar cy, yr, mn, dt, dy, hr, min, sec, msec , CPOL = 1; void set_spi () / * ----- enable DUT with SCLK preset based upon CPOL ----- * / {if (CPOL) {CS = 1; / * make sure CS is high * / SCLK = 1; / * set SCLK for CPOL = 1 * / CS = 0; / * enable DUT * /} else {CS = 1; / * make sure CS is high * / SCLK = 0; / * set SCLK for CPOL = 0 * / CS = 0; / * enable DUT * /}} void reset_spi () / * ----- reset DUT using SPI protocol ----- * / {if (CPOL) {CS = 1; SCLK = 1;} else {CS = 1; SCLK = 0;}} void wbyte_spi (uchar W_Byte) / * ----- write one byte to DUT ----- * / {uchar i; CS = 0; if (CPOL) {for (i = 0; i <8; ++ i) {DIN = 0 ; if (W_Byte & 0x80) {DIN = 1;} SCLK = 0; SCLK = 1; W_Byte << = 1;}} else {for (i = 0; i <8; ++ i) {DIN = 0; if (W_Byte & 0x80) {DIN = 1;} SCLK = 1; SCLK = 0; W_Byte << = 1;}}} uchar rbyte_spi (void) / * ----- read one byte from DUT ---- -* / {uchar i; uchar R_Byte; uchar TmpByte; R_Byte = 0x00; DOUT = 1; / * set up port for read * / CS = 0; if (CPOL) {for (i = 0; i <8; + + i) {SCLK = 0; TmpByte = (uchar) DOUT; SCLK = 1; R_Byte << = 1; R_Byte | = TmpByte;}} else {for (i = 0; i <8; ++ i) {SCLK = 1; TmpByte = (uchar) DOUT; SCLK = 0; R_Byte << = 1; R_Byte | = TmpByte;}} return R_Byte;} void writebyte () / * ----- write one byte, prompt for address and data ------ * / {uchar add; uchar dat; / * Get Address & Data * / printf ("Enter the Read Address ADDRESS (1,2,3 ...):"); scanf ("% bx", & add); printf ("DATA (0-ff):"); scanf ("% bx", & dat); set_spi (); wbyte_spi (add); wbyte_spi (dat); reset_spi (); } void initialize () / * ----- init clock data using user entries ----- * / / * Note: NO error checking is done on the user entries! * / {set_spi (); wbyte_spi (0x0f) ; / * control register write address * / wbyte_spi (0x00); / * clear write protect * / reset_spi (); printf ("Enter the year (0-99):"); scanf ("% bx", & yr); printf ("Enter the month (1-12):"); scanf ("% bx", & mn); printf ("Enter the date (1-31):"); scanf ("% bx", & dt); printf ("Enter the day (1-7):"); scanf ("% bx", & dy); printf ("Enter the hour (1-23):"); scanf ("% bx", & hr); hr = hr & 0x3f; / * force clock to 24 hour mode * / printf ("Enter the minute (0-59):"); scanf ("% bx", & min); printf ("Enter the second (0- 59): "); scanf ("% bx ", & sec); set_spi (); wbyte_spi (0x3f); / * clock burst write * / wb yte_spi (sec); wbyte_spi (min); wbyte_spi (hr); wbyte_spi (dt); wbyte_spi (mn); wbyte_spi (dy); wbyte_spi (yr); wbyte_spi (0); / * control * / reset_spi (); set_spi (); wbyte_spi (0x13); wbyte_spi (0x20); / * century data * / reset_spi ();} void disp_clk_regs () / * --- loop reading clock, display when secs change --- * / {uchar mil, pm, prv_sec = 99; while (! RI) / * Read & Display Clock Registers * / {set_spi (); wbyte_spi (0xbf); / * clock burst read * / sec = rbyte_spi (); min = rbyte_spi (); hr = rbyte_spi (); dt = rbyte_spi (); mn = rbyte_spi (); dy = rbyte_spi (); yr = rbyte_spi (); cy = rbyte_spi (); / * dummy read of control register * / reset_spi (); set_spi () ); wbyte_spi (0x93); / * century byte read address * / cy = rbyte_spi (); reset_spi (); if (hr & 0x80) mil = 0; else mil = 1; if (sec! = prv_sec) / * display every time seconds change * / {if (mil) {printf ("% 02bX% 02bX /% 02bX /% 02bX% 01bX", cy, yr, mn, dt, dy); printf ("% 02bX:% 02bX:% 02bX ", hr, min, sec);} else {if (hr & 0x20) pm = 'P'; else pm = 'A'; hr & = 0x1f; / * strip mode and am / pm bits * / printf ("% 02bx% 02bx /% 02bx /% 02bx% 02bx", cy, yr, (mn & 0x1f), dt, dy); printf ("% 02bx:% 02bx: % 02bx% cM ", hr, min, sec, pm);}} prv_sec = sec;} RI = 0; / * Swallow keypress to exit loop * /} void burstramread () / * ------ read RAM using burst mode ----- * / {uchar k; printf ("MAX6901 RAM contents:"); set_spi (); wbyte_spi (0xff); / * ram burst read * / for (k = 0; k <31; k ++) {if (! (k% 8)) printf (""); printf ("% 02.bX", rbyte_spi ());} reset_spi ();} void burstramwrt (uchar Data) / * ---- -write RAM using burst mode ------- * / {uchar k; set_spi (); wbyte_spi (0x7f); / * ram burst write * / for (k = 0; k <31; k ++) {wbyte_spi (Data);} reset_spi ();} main (void) / * ---------------------------------- ------------------- * / {uchar i, M, M1; while (1) {printf ("MAX6902 build% s", __DATE__); printf ("CI . Initialize MAX6902 "); printf (" CW. Write Byte "); printf (" CR. Read Time "); printf (" RW. Write RAM "); printf (" RR. Read RAM "); printf (" Enter Menu Selection: "); M = _g etkey (); switch (M) {case 'C': case 'c': printf ("Enter Clock Routine to run: C"); M1 = _getkey (); switch (M1) {case 'I': case ' i ': initialize (); break; case' R ': case' r ': disp_clk_regs (); break; case' W ': case' w ': writebyte (); break;} break; case' R ': case 'r': printf ("Enter Ram Routine to run: R"); M1 = _getkey (); switch (M1) {case 'R': case 'r': burstramread (); break; case 'W': case 'w': printf ("Enter the data to write:"); scanf ("% bx", & i); burstramwrt (i); break;} break;}}}
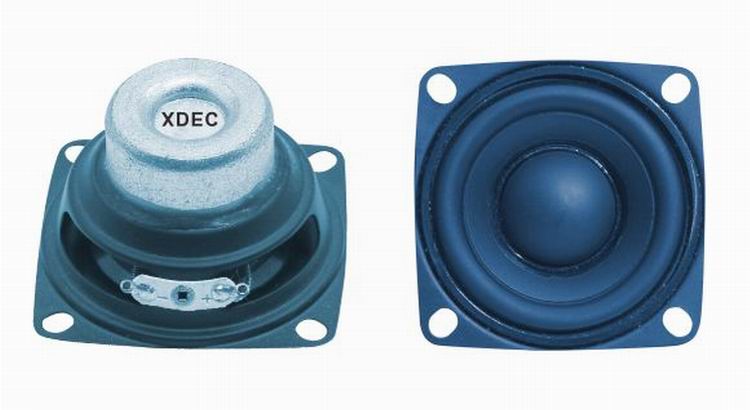
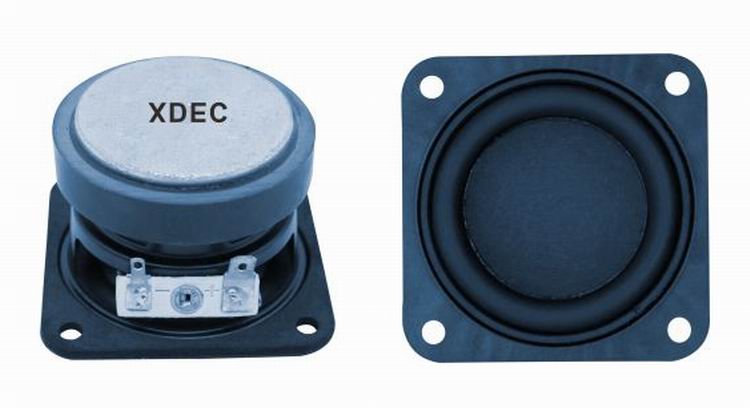


XDEC: 2000pcs for one model.
Q2. What is the delivery lead time?
XDEC: 15 days for normal orders, 10 days for urgent orders.
Q3. What are the payment methods?
XDEC: T/T, PayPal, Western Union, Money Gram.
Q4. Can you offer samples for testing?
XDEC: Yes, we offer free samples.
Q5. How soon can you send samples?
XDEC: We can send samples in 3-5 days.
Abstract: This application note provides hardware and software design examples for the interface between the MAX6902 and 8051 microcontroller.