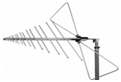
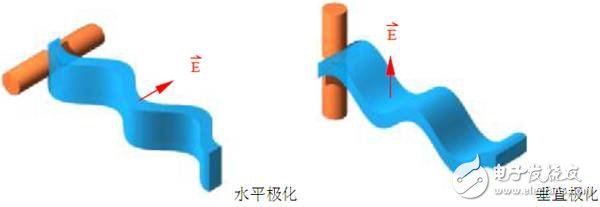
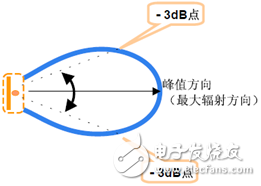
Antennas are widely used in EMC, RF testing, and measurement. Common antennas are as follows: 1. Double cone antenna: Often used in RSE alternative testing. Common working frequency band: 30MHz~300MHz 2, logarithmic antenna: Commonly used for NSA calibration of radiation sites. Common working frequency band: 30MHz~1GHz 3. Logarithmic period antenna: Commonly used for radiated disturbance/radiation spurious low frequency testing. Common working frequency band: 30MHz~3GHz 4, three-ring antenna: Commonly used in field testing of luminaire products. Common working frequency band: 9KHz~30MHz 5, horn antenna: Commonly used for radiated disturbance/radiation spurious high frequency testing. Common working frequency band: 1GHz~18GHz 6, dipole antenna: Commonly used in the measurement of site attenuation and antenna coefficients. Common working frequency band: 30MHz~4GHz 7, ring antenna: Commonly used for low frequency magnetic field testing. Common working frequency band: 9KHz~30MHz In conducting EMC and RF testing, the following basic concepts need to be mastered: 1. Polarization direction of the antenna Frequently, customers ask what is vertical and what is horizontal. The antenna radiates electromagnetic waves to the surrounding space. Electromagnetic waves are composed of an electric field and a magnetic field. It is stipulated that the direction of the electric field is the direction of polarization of the antenna. Generally used antennas are unipolar. The figure below shows two basic single-polarization cases. 2, the width of the lobe The beam width refers to the angle between the two half power points in the direction of the peak response of the antenna. The beam width has two components, the E plane and the H plane. The two are not necessarily equal. If the gain of an antenna is designed as Positive, its beamwidth and gain are often just the opposite. The pattern usually has two or more lobes, of which the lobes with the highest radiance are called the main lobes and the others are called the side lobes or side lobes. The angle between two points where the radiation intensity is reduced by 3 dB (half the power density) on both sides of the maximum radiation direction of the main lobe is defined as the lobe width (also known as beam width or main lobe width or half power angle). The narrower the lobe width, the better the directivity, and the farther the action distance is, the stronger the anti-interference ability is. 3, antenna gain Gain is the ratio of the power density of the signal produced by the actual antenna at the same point in space as the ideal radiating element, under the condition of equal input power. It quantitatively describes the extent to which an antenna concentrates the input power. The gain is obviously closely related to the antenna pattern. The narrower the main lobe of the pattern, the smaller the side lobes and the higher the gain. The physical meaning of the gain can be understood in this way - to generate a signal of a certain size at a certain distance over a certain distance, if an ideal non-directional point source is used as the transmitting antenna, 100 W of input power is required, and the gain is G. When a directional antenna with 13 dB = 20 is used as the transmitting antenna, the input power is only 100 / 20 = 5W. In other words, the gain of an antenna, in terms of the radiation effect in its maximum radiation direction, is a multiple of the input power amplification compared to an ideal point source with no directivity. 4, antenna coefficient (AF) The antenna coefficient in free space is a parameter inherent to the antenna itself. The antenna coefficient represents the relationship between the radiation field of the antenna and the input voltage of the antenna. AF has the following relationship with the gain: AF=E/U (E- electric field strength of a uniform plane wave incident on the reference plane of the receiving antenna; U-receiver antenna output voltage) 5, bandwidth Bandwidth refers to the frequency coverage of the antenna. If the bandwidth is expressed as part of the rated frequency range of the antenna, the bandwidth of the non-resonant antenna is greater than the bandwidth of the resonant antenna. The bandwidth of the low-gain antenna is greater than the bandwidth of the high-gain antenna. An antenna of a balanced unbalanced converter or matching network whose bandwidth is more affected than the antenna coefficient. 6, impedance The impedance of the antenna is usually considered very small, because the load impedance of all EMC test equipment is designed to be 50Ω. The impedance of the EMC antenna is usually designed to be close to 50Ω in the frequency range. However, the tester should also be aware of the impedance. The possible problems caused by matching, especially for low-frequency magnetic field loop antennas, the impedance of the antenna tends to vary with frequency, but many low-frequency loop antennas do not match the network to compensate for this change. 7, standing wave ratio (VSWR) The standing wave ratio is an indirect parameter that measures whether the impedance of two RF devices matches. VSWR is very important for most users. There are several complications. In simple terms, the impedance exhibited by the feeder is the sum of the magnitude and load impedance of the feeder. Therefore, at both ends of the feeder. Impedance mismatches may occur so that most of the signal will be reflected at the load and then re-reflected at the source along the feeder, when accurate measurements are required, or when the source is sensitive to impedance mismatch At the time, or when the loss of the feeder is very heavy, VSWR will become a problem. 8, size Size is an important antenna characteristic. The antenna needs to be controlled and moved to limit the actual size of the antenna. The use of the antenna in the shielding room also limits the maximum size of the antenna. It is necessary to reduce the undesired ground or surrounding objects. Coupling will also affect the size, but conversely, it is desirable to have a good low frequency response, high gain or wide bandwidth to increase the size of the antenna. Sewing Machine Servo Motor,Dorna Servo Motor,Industrial Motor,Brushless Sewing Machine Motor LISHUI SHUANGZHENG MOTOR CO.,LTD. , https://www.szservomotor.com