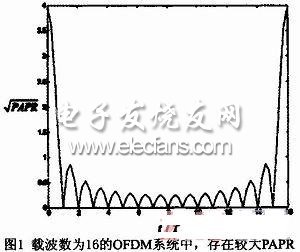
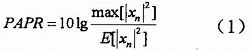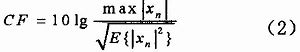The article proposes some related suppression techniques for the peak-to-average ratio existing in the OFDM system, which improves the reliability and effectiveness of the system. In practical applications, the appropriate method can be selected according to requirements and needs. 1 Definition of peak-to-average ratio in OFDM system An OFDM symbol is formed by adding multiple independent modulated subcarrier signals. At a certain moment, if multiple subcarriers are accumulated in the same direction, a relatively high peak-to-average power ratio (Peak- to-Average Power RaTIo, PAPR), referred to as peak-to-average ratio. For an OFDM system containing N sub-channels, when N sub-signals are summed in the same phase, the peak power of the resulting signal will be N times the average power. As shown in Figure 1, in this example, the peak-to-average power is 16 times the average power, in which all subcarriers are modulated by the same data symbol. We define the peak-to-average ratio as the ratio of the peak power of OFDM to its average power, namely: Among them, xn represents the output signal obtained after IFFT transformation in the OFDM system. The peak-to-average ratio of the baseband signal can be expressed as PART = 10lgN, when N = 256, PAPR = 24dB, of course, this is only an extreme case, the peak-to-average ratio in OFDM systems usually does not reach this value. We also use the crest factor to describe the peak change of the signal, which is defined as the ratio of the maximum signal value to the root mean square value: Shenzhen Kaixuanye Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.iconlinekxys.com