There are three types of mobile TV, one is based on the analog TV broadcast network, the other is based on the mobile communication network, and the other is based on the digital broadcast network. The first solution is to add an analog TV module to the mobile phone to receive analog TV broadcast programs. Because the effect is not satisfactory, it is not easy for consumers to accept. The scheme based on the mobile communication network is divided into a unicast scheme based on the 2.5G mobile communication network and a multicast scheme based on the 3G mobile communication network. The unicast solution uses the 3GPP standard video format and provides on-demand, live broadcast, and carousel services through streaming media servers, such as the WAP portals of China Mobile and China Unicom. Multicast solutions such as MediaFLO from Qualcomm of the United States, which calculates the load of the mobile network, performs reasonable network scheduling, and controls the playback time and transmission method of media programs. There are three major standards for mobile TV based on digital TV broadcasting networks: DVB-H (Digital Video BroadcasTIng-Handheld) in Europe, ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital BroadcasTIng-Terrestrial) in Japan, and T-DMB (Terrestrial-Digital MulTImedia in South Korea) BroadcasTIng). China's national standards have not been officially promulgated yet. Best Smartwatch Best Smartwatch everyone enjoys luck , https://www.eeluck.com
At present, T-DMB has been opened and operated in South Korea, with more than 300,000 users. Beijing, Guangdong and Shanghai are already constructing the T-DMB experiment network. DVB-H also started operations in several European countries. This article discusses the mobile TV program based on the digital TV broadcast network mobile phone, which consists of TI's DM275, HOLLYWOOD DTV1OOx and TSC2110 mobile phone platform.
Mobile digital TV mobile phone design
Mobile digital TV mobile phone contains two subsystems: DVB-H mobile digital television subsystem and GSM / GPRS communication subsystem, as shown in Figure 1. The two subsystems use the application processor as the host to control the DVB-H mobile digital TV receiver and GSM / GPRS communication module. 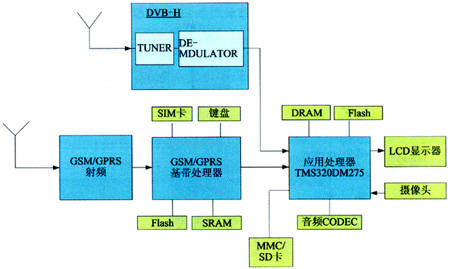
Figure 1 Mobile digital TV mobile phone block diagram
Mobile Digital TV Subsystem
The mobile digital TV system consists of a mobile digital TV receiver including a tuner, a demodulator and an application processor, as shown in Figure 2. 
Figure 2 Digital TV module functional block diagram
The input of a mobile digital TV receiver is a radio frequency broadcast signal from an antenna, and its output is an MPEG-2 transport stream (TS) or IP data packet. They are then input to the application processor for decompression of video and audio, and displayed on the LCD. The data communication on the interface between the mobile digital TV receiver and the application processor (TI DM275) is divided into two categories: (1) Control and state exchange. The application processor initiates program download and configuration for the receiver; the receiver reports the running information and status of the application processor. (2) Data flow. Transmit the channel signal to be decoded, including digital video, digital voice and data sent from the receiver to the application processor. The above two types of data are transmitted on one physical interface or two physical interfaces. There are three physical interface modes, as listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Physical interface mode 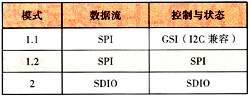
The following discusses the SDIO interface between the receiver and the application processor, as shown in Figure 3. 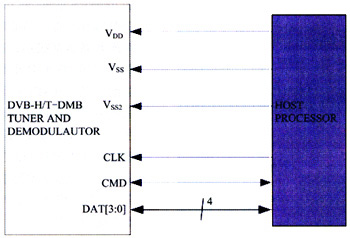
Figure 3 The receiver uses a 4-bit data line SDIO interface
In the SDIO interface mode, control and status reports and data streams are exchanged through SDIO, and are divided into 4-bit and 1-bit data interface modes, as listed in Table 2.
Table 2 SDIO interface mode 
The DSP core integrated on the DM275 is TMS320C54x, and the CPU core is ARM7TDMI. DM275 is a portable terminal DSP that supports H.264 / MPEG-4 AVC (hereinafter referred to as H.264) codec processing, and is characterized by the integration of a dedicated circuit responsible for MPEG-2 transmission code stream separation processing.
DM275 is the follow-up product of TI's TMS320DM270. It contains a dual-core structure of 102MHz TMS320C54x DSP processor and 88MHz ARM7TDMI microcontroller. The processing circuit for separating the MPEG-2 transmission code stream is added, and the dedicated circuit iMX, which is responsible for the decoding processing of part of the image data, also supports H.264 decoding processing.
The codec processing capabilities of DM275 are as follows: (1) Encoding processing. MPEG-4 Simple Profile: 640 × 480 pixels, 30 frames / s; MPEG-4 Advanced Simple Profile: 320 × 480 pixels, 30 frames / s. (2) Decoding process. H.264: 352 × 288 pixels, 30 frames / s; MPEG-4 Advanced Simple Profile: 720 × 480 pixels, 30 frames / s; MPEG-2: 720 × 480 pixels, 30 frames / s; DivX: 720 × 480 Pixels, 30 frames / s; WMV (Windows Media Video) 9: 720 × 480 pixels, 30 frames / s.
DM275 has a variety of external interfaces: USB, UART, MMC / SD, SPI, SDRAM, LCD. Can directly bring CCD or CMOS camera. Due to DM275's flexible programming features and strong signal processing capabilities, it can adapt to the needs of various standards of mobile TV standards and is suitable for mobile TV multimedia mobile phone applications.
GSM / GPRS communication subsystem
The GSM / GPRS communication subsystem is composed of radio frequency and baseband, and the baseband is composed of analog baseband and digital baseband. The baseband also controls peripheral circuits, including the SIM card, keyboard, flash memory, and SRAM. Power management, charging management, voice input and output, etc. are also controlled by the baseband. This module is based on the TSC2110 platform of TEXAS INSTRUMENTS. TI's mobile phone platform is the most widely used mobile phone platform in the world. Beijing Shouxin Co., Ltd. has been developing mobile phones on TI's mobile phone platform for more than 5 years and has rich experience in TI platform development. Therefore, the selection of TSC2110 can quickly integrate mobile digital TV mobile phones.
Connection between GSM / GPRS communication subsystem and mobile digital TV subsystem
The connection mode between the GSM / GPRS communication subsystem and the mobile digital TV subsystem is shown in Figure 4, which is to connect the GSM / GPRS digital baseband with the mobile digital TV application processor through a 16-bit parallel data line and a 17-bit parallel address line Connected. The DM275 works in the external main processing mode, and the GSM / GPRS digital baseband accesses the DM275 through the external main CPU interface. DM275 can work in bypass mode, stop power supply to DM275, GSM / GPRS digital baseband can directly drive LCD display, reduce standby power consumption. 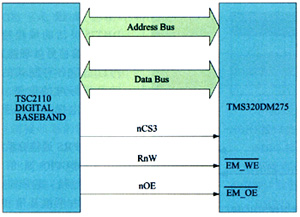
Figure 4 GSM / GPRS communication subsystem and mobile digital TV subsystem connection diagram
Mobile digital TV test plan
Testing of mobile digital TV mobile phones, including GSM / GPRS communication function test and DVB-H digital TV function test. The test scheme of GSM / GPRS communication function is very mature, only the DVB-H TV function test is discussed here. The MDTV test includes work verification and performance verification. Work verification refers to the complete reception of the signal under ideal conditions; performance verification refers to the signal reception capability at the DVB-H terminal.
Basic requirements for DVB-H / T work verification
(1) broadcast DVB-H / T signal of 1 TV program; (2) complete MPE FEC; (3) time slicing (TIME SLICING); (4) support PSI / SI; (5) work in UHF frequency band. For performance verification, it is also necessary to support VHF and L-band and insertion attenuation.
Simple device for DVB-H / T work verification
In a simple device for DVB-H / T work verification, all data is recorded in a computer and transmitted to a modulator that provides RF signals. This device can evaluate DVB-H / T reception regardless of the content of the transmission Device. The device is shown in Figure 5. 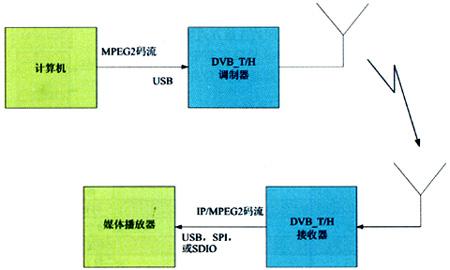
Figure 5 Simple device for DVB-H / T work verification
The laptop computer stores the recorded data stream and sends it to the modulator via USB. There are two types of recorded data streams: (1) The data stream recorded for DVB-T. The video and audio stream in MPEG-2 format is encapsulated into an MPEG-2 transport stream file, and this file contains the PSI / SI table. (2) Data stream recorded for DVB-H. H.264 video and AAC audio formats are encapsulated into MPEG-2 transport stream files, and also contain PSI / SI tables.
The DVB-T / H RF modulator converts the DVB asynchronous bit stream into an RF signal. It performs the following functions: up-conversion, modulation, and overall control of the entire DVB-H / T physical layer parameters. It is recommended to use Enensys' NN6-1161 modulator.
The DVB-H / T receiver being evaluated is connected to a computer or embedded platform via USB or SDIO, SPI. The computer serves two functions: receiving and playing the multimedia stream; diagnostic retrieval and monitoring of the DVB-H / T receiver. The software package installed on the computer can play the content and retrieve the diagnosis. The software package also allows users to monitor and control the following parameters: RF tuner parameters (frequency, gain, etc.); demodulator control parameters (such as FFT mode, guard interval, etc.); DVB-H / T connection layer (MPE-FEC) parameters (Such as BURST size, time slice length, etc.).
Advanced device for DVB-H / T work verification
The advanced device for DVB-H / T work verification is shown in Figure 6. The laptop computer stores the recorded data stream and outputs it through the network connection. The data stream is recorded in H.264 format and sent via RTP / UDP. The IP packetizer (IPE) converts the IP stream into a DVB asynchronous bit stream. Perform the following tasks: multi-protocol packetization, section packaging, time slicing, and PSI / SI insertion. The IP packetizer recommends the DP14502 from DataPlanet. 
Figure 6 DVB-H / T work verification advanced device
The DVB-T / H RF modulator converts the DVB asynchronous bit stream into an RF signal. It performs the following functions: up-conversion, modulation, and overall control of the entire DVB-H / T physical layer parameters. It is recommended to use Enensys' NN6-1161 modulator.
DVB-H / T performance verification device
This device uses R & S's broadcast test system SFU, as shown in Figure 7. This device can also be used as an advanced platform for controlling channel parameters directly related to the air interface. These parameters include output level, attenuation, RF frequency sweep, fading effects, and additive noise. 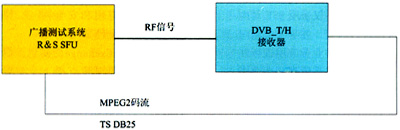
Figure 7 DVB-H / T performance verification device
R & S's broadcast test system provides complete DVB-H / T signals, including the ability to configure different broadcast modes and modulation parameters. The RF signal output by the test system can be directly input to the DVB-H receiver or transmitted to the air. The transmission code stream output by the DVB-H receiver is sent back to the broadcast test system to compare the data sent and received to obtain the performance of the DVB-H receiver under intermediate conditions. This device is mainly used to measure the decoded signal quality under channel attenuation conditions, that is, to provide a means of evaluating and verifying the performance of DVB-H receivers.