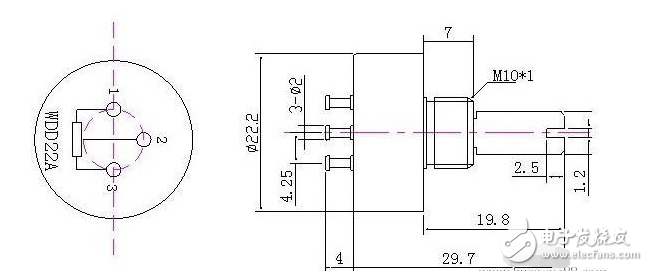
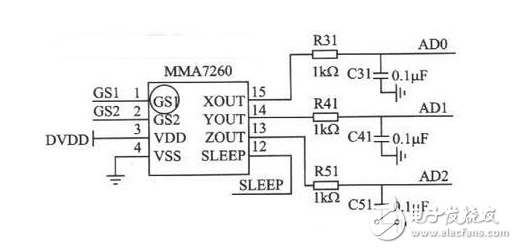
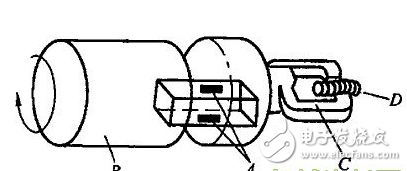
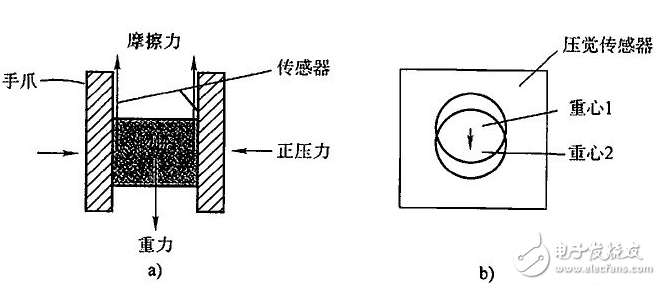
The general robot system consists of four interacting parts: the robot, the environment, the task, and the controller. We call the sensors that are typically mounted on the robotic robots as Inner Sensors, and the sensors that are part of the environment are External Sensors (External Sensons). The following will be based on this, combined with other classification methods of robot sensors. The robot industry has developed rapidly in recent years. In 2012, the global output was 160,000 units. The robot market in industrialized countries such as Europe, America and Japan has matured and is in a period of flat growth. The robot density (the number of robots used by 10,000 employees) is 347 in South Korea, 339 in Japan, 261 in France, and 10 in China (there are 21 statistical data, for reference only). The Chinese robot market has also developed rapidly. The annual growth rate of industrial robots has exceeded 20%. In 2010, the installed capacity was 52,290 units. In 2011, it increased to 74,317 units, achieving a growth rate of 42%. In 2012, China issued the “12th Five-Year Plan for Intelligent Manufacturing Technology Developmentâ€. On April 21, 2013, the “China Robot Industry Alliance†was also established. These all prove that China’s robot industry will have a bigger development of. Robot products are currently classified into two categories: industrial robots and service robots. There are two types of industrial robots and special robots in China; or two types: general robots and intelligent robots; or two types: general robots and mobile robots; or general robots and anthropomorphic robots. At present, industrial robots are mostly used for handling, sorting, loading and unloading, packaging, palletizing, welding, spraying, grinding, polishing, cutting, placing, assembly and so on. As the level of intelligence increases, more and more robotic sensors are used. There are three types of intelligent robots: interactive robots, sensor robots and autonomous robots. From the anthropomorphic function, vision, force and touch are the most important. It has already entered the practical stage, and the hearing has also made great progress. Others have sense of smell, taste, and slid. There are various sensors, so the robot sensing industry has also formed. Production and research strength. The control system of the robot is equivalent to the human brain, and the actuator is equivalent to human limbs. The sensor is equivalent to the facial features of human beings. Therefore, to make the robot receive and process external information like a human, the robot sensor technology is an important manifestation of robot intelligence. The sensor is a necessary means for the robot to complete the feeling. Through the sensory effect of the sensor, the relevant characteristics of the robot itself or the characteristics of the related object are converted into the information required by the robot to perform a certain function. Depending on the purpose and range of use of the sensor on the robot, it can be divided into internal sensors and external sensors. The internal sensor is used to detect the state of the robot itself (such as the angle between the arms, the position, speed and acceleration in the robot motion engineering); the external sensor is used to detect the external environment and object conditions of the robot, such as the shape of the captured object, Spatial position, whether there are obstacles, whether the object slips or not. Internal sensor Machine-mechatronics products, internal sensors and mechanical components such as motors and shafts or mechanical structures such as arm (arm), wrist (Wrist), etc. are installed together to complete the measurement of position, speed and strength to achieve servo control. Position (displacement) sensor The linear motion sensor has two types of potentiometer sensors and adjustable transformers. The angular displacement sensor has three types: a potentiometer type, a variable transformer (resolver) and a photoelectric encoder. The photoelectric encoder has an incremental encoder and an absolute encoder. The incremental encoder is generally used for zero-position uncertain position servo control. The absolute encoder can obtain the instantaneous value of the drive shaft corresponding to the initial lock position of the encoder. When the device is under pressure, just read each joint code. The reading of the servo can adjust the given value of the servo control to prevent excessive movement during the start of the robot. Speed ​​and acceleration sensor Speed ​​sensors measure both translational and rotational motion speeds, but in most cases are limited to measuring rotational speed. Using the derivative of the displacement, especially the photoelectric method, the light is irradiated to the rotating disk, the rotation frequency and the number of pulses are detected, the rotation angle is determined, and a gap is formed by the disk, and the angular velocity is recognized by the two photodiodes, that is, the rotation speed This is the photoelectric pulse speed sensor. In addition, there are speed measuring generators for speed measurement. A strain gauge, a telescopic gauge, is also a stress sensor for acceleration measurements. The acceleration sensor is used to measure the dynamic control signals of industrial robots. Generally, there is a power derived from the velocity measurement and the power generated by the acceleration of a known mass object, that is, the strain gauge is used to measure the force for deduction, and the following method is also performed: The force associated with the measured acceleration can be generated by a known mass. This force can be electromagnetic or electrodynamic, and is ultimately reduced to the measurement of the current. This is the servo return sensor, and actually there are a variety of vibrating acceleration sensors. Force sensor The force sensor is used to measure the three components of the force between the two objects and the three components of the moment. The ideal sensor in the robot is a semiconductor strain gauge bonded to the compliant component. Specifically, there are a metal resistance type force sensor, a semiconductor type force sensor, other magnetic pressure type, and a force sensor manufactured by the principle of string vibration. There are also torque sensors (such as the use of photoelectric sensors to measure torque), wrist force sensors (such as the International Stanford Research Institute consists of six small differential transformers, can measure the power in the three directions of the wrist X, Y and Z and Each axis dynamic torque). Due to the long history of robot development, AC servo systems based on AC permanent magnet motors have been widely used in recent years. Sensors corresponding to position and speed are widely used in various types of photoelectric encoders, magnetic encoders and resolvers. External sensor In the past, general industrial robots have no external sensory ability, and new generation robots such as multi-joint robots, especially mobile robots and intelligent robots, require the ability to correct and change the reaction environment. External sensors are capable of realizing these capabilities. Tactile sensor Microswitches are the most common type of contact sensors, as well as isolated two-state contact sensors (ie, bistable switching semiconductor circuits), single analog sensors, matrix sensors (matrix sensors for piezoelectric elements, artificial skin - variable conductivity polymers) , light reflection tactile sensor, etc.). Stress sensor For example, when the multi-joint robot is moving, it is necessary to know the actual contact, the position of the contact point (positioning), and the characteristics of the contact, that is, the estimated force (characteristic). Therefore, the strain gauges indicated in the previous section are combined with the specific conditions. The basic assumptions of stress detection, such as the determination of the force between the work surface and the object, specifically the installation of sensors for the environment, the installation of test equipment transmission device for the wrist of the robot as a sensor. Proximity sensor Since the moving speed of the robot is increased and the loading and unloading of the object may cause damage, etc., it is necessary to know the a priori information of the position of the object in the working place of the robot and the appropriate trajectory planning, so it is necessary to apply a remote sensing method for measuring the proximity. Proximity sensors are divided into passive and active sensors, so in addition to natural sources, transmitters and receivers of artificial signals may be required. An ultrasonic proximity sensor is used to detect the presence and measurement distance of an object. It can't be used to measure distances less than 30~50cm, but the range is large. It can be used on mobile robots or on the handles of large robots. It can also be made into an ultrasound navigation system. The infrared proximity sensor, which is small in size and only a few cubic centimeters in size, can be mounted on the robotic gripper. Acoustic sensor Used to sense and interpret sound waves in a gas (non-contact sensation), liquid or solid (contact sensation). The sonic sensor complexity can range from simple sound wave detection to complex acoustic frequency analysis until individual speech and vocabulary recognition in continuous natural language. Contact or non-contact temperature sensor In recent years, it has been widely used in robots. In addition to commonly used thermal resistors (thermistors), thermocouples, etc., thermoelectric TV cameras have also made progress in measuring and sensing temperature images. Sliding sensor Used to detect the sliding of an object. When the robot is required to grasp an object of unknown characteristics, it is necessary to determine the most appropriate grip value, so it is required to detect an object slip signal generated when the grip strength is insufficient. Use this signal to firmly grasp the object without damaging the object. There are currently a sliding sensor using an optical system and a sliding sensor using a crystal receiver whose detection sensitivity is independent of the sliding direction. distance sensor Distance sensors for intelligent mobile robots include laser range finder (which can also measure angles) and sonar sensors, which have been developed in recent years. Vision sensor It emerged in the late 1950s and developed very rapidly. It is one of the most important sensors in robots. Machine vision began to deal with the world of building blocks from the 1960s and later to the real world of outdoor processing. After the 1970s, a practical visual system emerged. Vision generally consists of three processes: image acquisition, image processing, and image understanding. Relatively speaking, image understanding technology is still very backward. Dynamic range: refers to the range that the sensor can detect. For example, if the current sensor can measure the current from 1mA to 20A, then the measuring range of this sensor is 10log(20/0.001)=43dB. If the input of the sensor is beyond the measuring range of the sensor, the sensor will not display the correct measured value. For example, an ultrasonic sensor cannot measure a close object. Resolution: Resolution is the smallest difference a sensor can measure. For example, a current sensor, which may have a resolution of 5 mA, that is, a current difference of less than 5 mA, which cannot be detected. Of course, the higher the resolution of the sensor, the more expensive it is. Linearity: This is a very important indicator to measure the relationship between sensor input and output. Frequency: refers to the sampling speed of the sensor. For example, an ultrasonic sensor has a sampling speed of 20 Hz, which means that it can be scanned 20 times per second. Robot sensor requirements and options The choice of the robot sensor depends on the robot's working needs and application characteristics, and the basic basis for selecting the sensor when it is required for the robot's sensory system. High precision and good repeatability; Good stability and reliability Strong anti-interference ability; Light weight, small size and easy installation. All the robot sensors are closely related to the signal transformation and processing after the detection of the signal, and the software for the conversion processing is very large, and it is also integrated with the information technology such as artificial intelligence. Therefore, this article is only a sneak peek, and needs to be further explored.
Gan chargre
Gallium nitride, or GaN, is a material that's starting to be used for semiconductors in chargers.The main thing about GaN when it comes to chargers is that it produces less heat.Ultimately, this means your devices will charge faster with a GaN charger than with a silicon one. In summation, GaN chargers are more power efficient, significantly smaller, and capable of charging your devices much faster than a silicon-based charger.
Gan Fast Charger,Best Gan Charger,Baseus Gan Charger,Anker Gan Charger,Usb to Usb Charger Pogo Technology International Ltd , https://www.wisesir.net