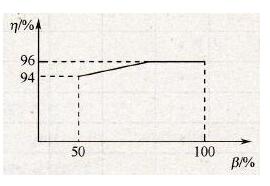
The choice of inverter capacity is an important and complicated problem. It is necessary to consider the matching between inverter capacity and motor capacity. The small capacity will affect the output of the effective torque of the motor, affect the normal operation of the system, and even damage the device. The harmonic component of the current increases, which also increases equipment investment. The basic principles for selecting the drive capacity are as follows. 1, the principle of matching The choice of frequency converter should match the load. The performance is as follows. (1) Power matching: The rated power of the inverter is consistent with the rated power of the load; it should be noted that the power requirements of the motor are different. For example, for motors of the same power, the capacity of the inverter required for different load characteristics is also different. The inverter capacity required for the square torque load (fan) is lower than the inverter capacity required for the constant torque load. Generally, the inverter product specification directly gives the rated power or apparent power suitable for driving the motor. Therefore, for a square torque load such as a fan or a pump, the corresponding inverter can be selected according to the motor power. (2) Voltage matching: The rated voltage of the inverter matches the rated voltage of the load. (3) Current matching: Ordinary centrifugal pump, the rated current of the inverter is matched with the rated current of the motor; for special loads, for example, deep water pumps, the performance parameters of the motor should be considered, and the current and overload capacity of the inverter should be determined by the maximum current. (4) Torque matching: Consider when using a constant torque load or when there is a reduction gear. 2. Economic principles Technical analysis and economic analysis should be carried out, and control schemes that meet the application requirements and have a high performance-price ratio should be selected. 3. Specific analysis of specific conditions For different application situations, specific analysis should be made and the inverter capacity should be determined. (1) Select the motor capacity according to the inverter product specification: In the following cases, the inverter capacity can be selected according to the inverter product specification. (2) When selecting the inverter capacity, you need to select the first gear or the second gear according to the capacity of the manual: In the following cases, you need to select the first gear or the second gear. (3) When using the inverter rated power as the inverter capacity index to select the inverter, since the influence of the number of motor poles and the rated current of the motor is not considered, when the inverter is selected according to the rated power of the inverter, the selected inverter may be selected. The rated current of the motor cannot be met. (4) When the rated current of the motor is used as the inverter for the inverter capacity, there is usually a certain margin when the motor capacity is not considered. Especially for the inverter modification project, the margin when the motor is selected is generally 40%~ 50%, therefore, depending on the rated current of the motor, the inverter capacity may be too large, which may cause the inverter to run under low load, resulting in waste of resources. In addition, the maximum operating current of the motor affects the heating and temperature rise of the motor. For short-time overload, the inverter has an overload capacity of 150% and 1 min. Therefore, for applications with large load fluctuations, the motor should be known when selecting the inverter. The maximum running current and overload time make the inverter not exceed its rated current at the maximum operating current, or the overload current when the overload time is less than 1 min is less than 150% of rated current. (5) Appropriate matching between the inverter and the motor means that the rated current (or maximum operating current) of the motor should be less than the rated current of the inverter under the same power. For example, from the table, the original 8-pole 18. 5kW motor is selected from the same power inverter. Because of the large fluctuation of the load, ABB's ACS800 series products are selected. (6) When the inverter capacity is reduced, pay attention to the impact of the motor starting current and acceleration current. To this end, it is considered to add an output reactor between the inverter and the motor to smooth the inrush current and the acceleration current, reduce the impact of the inrush current and the acceleration current; and accelerate the acceleration and deceleration of the production process. And the deceleration time setting is longer; the preset value of U/f is set smaller when starting. (1) Understand the nature of the load and the law of variation, calculate the magnitude of the load current or make a load current diagram I=f(t); (2) Preselect the inverter capacity; (3) Verify the pre-selected inverter and verify the overload capability and starting capability if necessary. If both pass, the pre-selected inverter capacity is selected; otherwise, restart from (2) until it passes. Under the premise of meeting the requirements of production machinery, the smaller the inverter capacity, the more economical. There are many misunderstandings in the actual operation of the inverter's capacity selection. Here are three basic capacity selection methods that complement each other. (1) From the perspective of current Most drive capacities can be expressed from three angles: rated current, available motor power and rated capacity. Among the latter two, the inverter manufacturer is given by the standard motor produced by the country or the company, or it is reduced with the output voltage of the inverter, it is difficult to accurately express the capability of the inverter. When selecting a frequency converter, only the rated current of the frequency converter is a critical quantity reflecting the load capacity of the semiconductor inverter. The load current does not exceed the rated current of the inverter is the basic principle for selecting the capacity of the inverter. It is important to note that before determining the inverter capacity, the process conditions and motor parameters of the equipment should be carefully understood. For example, the rated current of the submersible pump and the wound rotor motor is greater than the rated current of the common cage asynchronous motor, and the roller table commonly used in the metallurgical industry. The motor is not only rated at a much larger current, but it is also allowed to be in a stalled state for a short time, and the roller conveyor is mostly multi-motor transmission. It should be ensured that the total current of the load is not allowed to exceed the rated current of the inverter in the non-fault state. (2) From the perspective of efficiency The system efficiency is equal to the product of the efficiency of the inverter and the efficiency of the motor. Only when both are operating at higher efficiency, the system efficiency is higher. From the perspective of efficiency, the following points should be noted when selecting the inverter power: 1) The inverter power value is equivalent to the motor power value, so that the inverter can run at high efficiency value; 2) When the power classification of the inverter is different from the motor power classification, the power of the inverter should be as close as possible to the power of the motor, but should be slightly larger than the power of the motor; 3) When the motor is frequently started, braked, or is under heavy load and is working more frequently, a larger frequency converter can be selected to facilitate long-term and safe operation of the inverter; 4) After testing, the actual power of the motor does have a surplus. You can consider the inverter with power less than the motor power, but pay attention to whether the instantaneous peak current will cause overcurrent protection action; 5) When the inverter and motor power are not the same, the settings of the energy-saving program must be adjusted accordingly to achieve a higher energy-saving effect. The relationship between the load factor b of the inverter and the efficiency η is shown in the figure. Graph load rate versus efficiency curve It can be seen that when β=50%, η=94%; when β=100%, η=96%. Although β is doubled, the η change is only 2%, but it is also considerable for medium and high power, such as several hundred kilowatts to several thousand kilowatts. The system efficiency is equal to the product of the efficiency of the inverter and the efficiency of the motor. Only when both are operating at higher efficiency, the system efficiency is higher. (3) From the perspective of calculating power For continuous operation, the inverter must meet the following three calculation formulas. 1) Meet the load output: PCN ≥ PM / η. 2) Meet the motor capacity: PCN ≥ k 3kUeIe & TImes; 10-3. 3) Meet the motor current: ICN ≥ kIe. In the formula, PCN is the inverter capacity (unit is kVA); PM is the motor shaft output power (in kW) required by the load; Ue is the rated voltage of the motor (unit is V); Ie is the rated current of the motor (unit is A) η is the motor efficiency (usually about 0.85); cosφ is the motor power factor (usually about 0.75), and k is the current waveform compensation coefficient (since the output waveform of the inverter is not a complete sine wave, it also contains high order) 1)。 The composition of the harmonics, the current should be increased, usually k is 1. 05 ~ 1. 1). Motor Start Switch,Single Phase Motor Starter Switches,Single Phase Centrifugal-Switches,Electric Machine Centrifugal Switch Gear Ningbo Zhenhai Rongda Electrical Appliance Co., Ltd. , https://www.centrifugalswitch.com