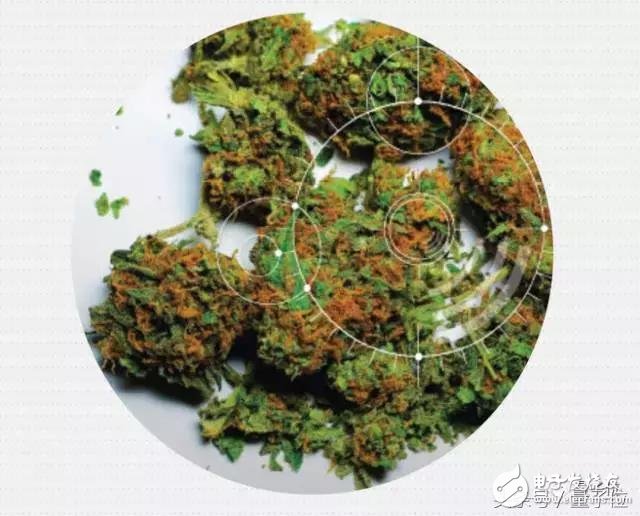
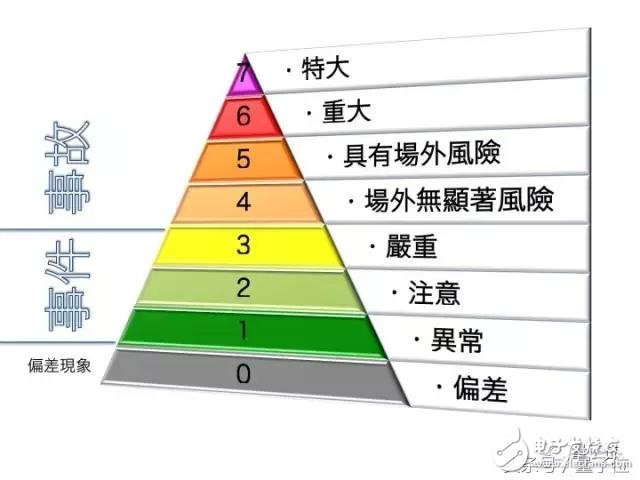
This is the best AI era. It lurks around us and facilitates modern life. Speech recognition, face unlocking, personal assistants, image beautification, recommendation sorting, disease prediction, fashion design, artistic creation, Mars exploration... AI has penetrated into every corner of our lives. There are also AI applications that you can't imagine, starting to sprout in some corner of the world. In July, NASA's Frontier Development Lab (FDL) announced that it would use AI to prevent asteroids from colliding with the Earth, saving the planet and protecting humanity. NASA can always hang a lot of sense of mission. This secret FDL bears the great mission of "looking for an asteroid that may threaten the safety of the planet and trying to solve it." This time, mainly AI is working hard. FDL first gathered together various industry scholars to discuss, and then use machine learning to simulate planetary orbits, and visualize 2D data research into 3D planetary operational images to determine their spin rate and shape, and whether it would endanger the Earth. What if I predict that I will hit the Earth? Currently, NASA has approved the "Dual Asteroid Redirection Test" (DART) technology, which is scheduled to launch a high-speed spacecraft into the double asteroid "Didymos" in 2020 to deflect its orbit. Not very powerful. Many people still talk about the nuclear power plant. The International Nuclear Energy Event Scale (INES) classifies the impact of nuclear power plant accidents on safety by level 7. The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident in 2011 is a super-class. So, can AI help us maintain nuclear power plants? What can it do? Recently, the French utility power company EDF intends to use AI to optimize the predictive maintenance of nuclear power plants. “First identify the components in the plant from the factory's sensors and why they will fail,†said David Ferguson, digital innovation director at EDF. More interestingly, they also intend to use AI to achieve real-time condition monitoring and provide some advice for managers. Perhaps in the future, nuclear power plants can achieve autonomous operations. This is not the first time that EDF has proposed the concept of "AI management." EDF has been using AI to build "digital copies" of nuclear power plants, such as digitally connected physical components that contain digital instruction manuals. At the same time, EDF has been testing AI performance and using it to identify and process measurement data. The range of controllable artificial intelligence applications is growing. The machine also knows "reading mind". Recently, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) developed a body motion tracking system and named it OpenPose. In this motion analysis, the computer will perform real-time attitude detection on humans and track changes in the movement of the mission. The computer needs to capture human arm, leg and even a tiny nod. By allowing robots to understand the state of people around them through the nuances of non-verbal communication, robots can better serve humans in social space. This technology helps the robot to judge what the human being is doing, how it feels, and whether it is willing to be disturbed. It can assist the unmanned vehicle to detect pedestrians on the side of the road, judge whether they want to cross the road or just want to stand on the side of the road. Public transportation; it can also provide new methods for the diagnosis and rehabilitation of conditional behaviors such as autism, dyslexia and depression. Reality application scenarios have presented a major challenge to this technology. In social situations, the number of tests is large and there are often physical contacts between people. Therefore, in the initial attempt, the effect of tracking and detecting multiple people in real time is not good. In response to this situation, the researchers used a "zero to complete" research method. First, put all the body parts captured in the same scene - arms, legs, face - and then assemble these "parts" of the body. Researchers have already published the code for this progress, and although the technology was born more than a month, more than 20 companies have expressed interest. Among them, there are also some unmanned car companies. First of all, under the popular science, marijuana is also divided into categories. The marijuana in the "XXX marijuana imprisonment" incident that often appears in news reports generally refers to cannabis for entertainment. The main effective chemical component is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and excessive consumption may cause hallucination dependence. I don't talk about that today. Medicinal marijuana refers to cannabis made from herbal medicines, which contains less THC. On the contrary, it has more medicinal cannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD), which can be used for analgesia and control of epilepsy, cancer, etc. disease. In countries such as the United States, medicinal cannabis is not a contraband and can be treated according to doctor's advice. At present, there are as many as 30,000 drugs containing medical cannabis. PotBot is a medical cannabis recommendation engine that finds studies related to cannabinoids, cannabis active compounds, etc. through artificial medical literature related to medicinal cannabis. Later, it used a unique algorithm to find the most suitable cannabis plants for the treatment of 37 conditions (such as insomnia, asthma and cancer) and to provide personalized advice to patients. PotBot was created by David Goldstein and Baruch Goldstein. Currently, PotBot apps can be downloaded from overseas through the iOS or Android app market. No one knows how much the social platform knows how secret you are. Every year, billions of netizens post posts, updates and moods on various social platforms. The social platform undoubtedly holds big data on user behavior. This opens up an unprecedented opportunity to use artificial intelligence to gather information from mass communication. This is not only fun, but also very useful. Psychologist MarTIn Seligman works at the Mental Health Center at the University of Pennsylvania. He and more than 20 psychologists, doctors, and computer experts use machine learning and natural language processing to screen data to measure the public's mental and physical health. The Seligman team collected nearly 30,000 users who were considered depressed in Facebook. Through machine learning algorithms, they found that self-description in the data is directly related to the degree of depression. With these studies, they can use the description to determine whether other users have a tendency to depression. Big data on social media can be used not only to perceive public sentiment, but also to predict user personality, income, and political ideology. According to Twitter, the team created a psychological map of the states of the United States based on five personality traits such as happiness, depression and trust. Social networks may know you better than objects. Creating new substances in the "Molecular Kitchen" Organic chemistry is a reverse reasoning work. Like the chef, first see a finished dish and then study how to make it. The same is true for chemists. They must first consider the final structure of the desired synthetic material, and then think about how to assemble it. At present, Marwin Segler, a graduate student at the University of Münster, Germany, and their friends are trying to simplify the process of molecular synthesis with AI – let AI learn to pick atoms from hundreds of building blocks, and based on thousands of synthetic rules. Connect them. However, it is easy to write these complex rules into binary code, so the Segler team devised a deep neural network program that learns how chemical reactions work through millions of examples, rather than programming under the hard rules of chemical reactions. "The more data you give it, the better it will be," Segler said. Over time, neural networks can learn to predict the optimal reaction steps in synthesis, give their own lines, and let the molecules synthesize from scratch. The Segler team tested the program with 40 different molecules and compared it to the traditional molecular design program, which proved that AI was 95% faster than the traditional method. Segler hopes to improve the drug production process in this way, and he will also go to a London pharmaceutical factory for further research and exploration. Humans create AI, and AI changes the world. Autism has always been a tricky challenge. Difficulties are difficult. The variants of dozens of genes that cause disease can only explain 20% of cases, while other possible variations may be related to 25,000 other genes. Currently, Princeton University computational biologist Olga Troyanskaya teamed up with the New York Simmons Foundation to consider AI to analyze human genes. Troyanskaya combines hundreds of data sets, including the activity of genes in specific cells, the mechanism of protein interactions, and the location of transcription factor binding sites and other key genomic features. Later, they used machine learning to create genetic interaction maps and compared known autism risk genes with hundreds of unknown genes to find similarities between the two. They published their papers in the journal Nature Neuroscience, proving that another 25,000 genes are associated with autism. To train this deep learning system, Troyanskaya graduate student Jian Zhou wrote "Encyclopedia of DNA Elements" and "Apparent Genomics", which compiled how tens of thousands of non-coding DNA sites affect neighboring genes. Exploring the secrets of the human genome and guiding research on known diseases, AI is slowly pushing for medical breakthroughs. Since the day when AI was applied to sex robots, it has earned the public eye. The world's first sex robot is Harmony of RealDoll, she can chat and move. In this sex robot revolution, artificial intelligence has been given a new task, allowing robots to try to become thinking, "passing people" and even feeling. At present, users can already set Harmony's personality through their mobile phones and adjust to the type they like. There are even custom-made children's sex robots that are exported from Japan and are not subject to legal restrictions in the United States (but were deducted by Canadian Customs). Professor Noel Sharkey of the University of Sheffield in the United Kingdom believes that sex robots will contribute to the occurrence of criminal acts such as rape and pedophilia. According to Professor Sharkey, robots are pre-programmed to resist sexual behavior and are actually simulating rape victims. Sharkey believes that sex robots can satisfy human sexual fantasies as much as possible, and gradually let humans lose their sense of guilt about rape and pedophilia, and encourage criminal behavior. "All these very human robots look like weird spiritual killers," Sharkey said. 48V30Ah Lithium Ion Battery,Long Cycle Life 48V 30Ah Battery,48V 30Ah Battery For Vehicle,Deep Cycle Life Battery Jiangsu Zhitai New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zt-tek.com