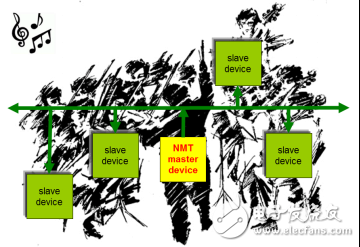
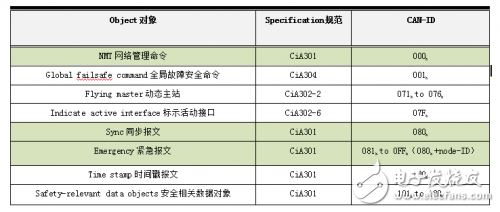
People use CAN instead of RS485, mainly because they can pay attention to the real-time advantage of burst transmission. In multi-node and long-distance applications, if there is no optimization, CAN bus and RS485 have no advantage, how to make CAN Communication is better than our traditional communication? Let CANOpen give you the answer. At the beginning of CANopen, even in the automotive electronics industry, which is the most widely used CAN bus, the number of CAN nodes and the information required to communicate in the network are relatively small. People use CAN instead of RS485, mainly focusing on the real-time advantage of burst transmission. In multi-node and long-distance applications, CAN bus and RS485 have no advantage, such as CAN communication under the same baud rate. The distance can only reach 0.6-0.8 times of RS485, and multi-node communication CAN can not perform arbitrary burst transmission, and has to follow the polling communication mechanism like RS485, otherwise it will cause congestion, as shown in Figure 1. Like this crossroads car, if there are only 10 cars, even if there is no traffic light, it will not be congested. And if there are 100 cars, if you drive at will, serious congestion will occur. Figure 1 CAN's sudden advantage and multi-node congestion The founder of CANopen is very familiar with the characteristics of CAN bus, so when designing CANopen, it is defined as real-time communication of small network and control signals: The message transmission adopts the CAN standard frame format. That is, the 11-bit ID field to minimize the transmission time; Network control messages use the minimum number of bytes of data. For example, a heartbeat message has only 1 byte of data; The process data updated in real time does not require a response from the recipient. That is to use the production consumption model to reduce the bus load; Configuration parameters that need to be acknowledged by the receiver are generally transmitted in fast words. That is, one message can transmit a maximum of one 32-byte parameter variable, which avoids the real-time degradation caused by the framing. These definitions are all designed to save time and maximize real-time performance. At the same time, in order to reduce the configuration workload of the simple network, CANopen defines a mandatory default identifier (CAN frame ID) allocation table to reduce the learning time of users and maintainers, and get started quickly. Although CANopen communication plays the role of CAN, all nodes have equal communication status and allow to send messages by themselves during operation. However, in order to be stable and reliable, CANopen network needs to set up a network management host NMT-Master (Network Management-Master). Like a conductor of a symphony orchestra, all nodes start and stop with his command, as shown in Figure 2. Figure 2 NMT-Master is like a symphony conductor The NMT host is generally a PLC or PC with monitoring in the CANopen network (of course, it can also be a general function node), so it also becomes a CANopen master station. The corresponding other CANopen nodes are NMT slaves (NMT-slaves). The message communicated between the NMT host and the NMT slave is called an NMT network management message. Management messages are responsible for layer management, network management, and ID distribution services. For example, initialization, configuration, and network management (including node protection). In network management, only one master node, one or more slave nodes are allowed in the same network, and the master-slave mode is followed. In addition, in order to coordinate the communication control of each node's synchronization, heartbeat, time, error prompt, etc., CANopen also defines a series of special protocols (Special protocols) messages. As shown in Table 1, NMT packets and special protocol packets are predefined for CANopen (Pre-defined CAN-IDs). Table 1 CAN-ID definitions for NMT and special protocols CAN-ID is the COB-ID of such messages. The readers must remember these common CAN-ID meanings of green shading. In the development and application of CANopen, these three types are the most commonly used NMT and special. Protocol message. The USBCAN-EP and PCI-5010-P master card can expand the CANOpen communication interface for the PC and realize the data communication of the CANOpen protocol. As the administrator of the CANOpen network, it implements all CANOpen Network Management (NMT) functions. Ev Charging Cable,Electric Car Charging Cable,Type 2 Charging Cable,32A Ev Charging Cable Yangzhou JERI New Energy Co., Ltd. , https://www.jrevcharging.com