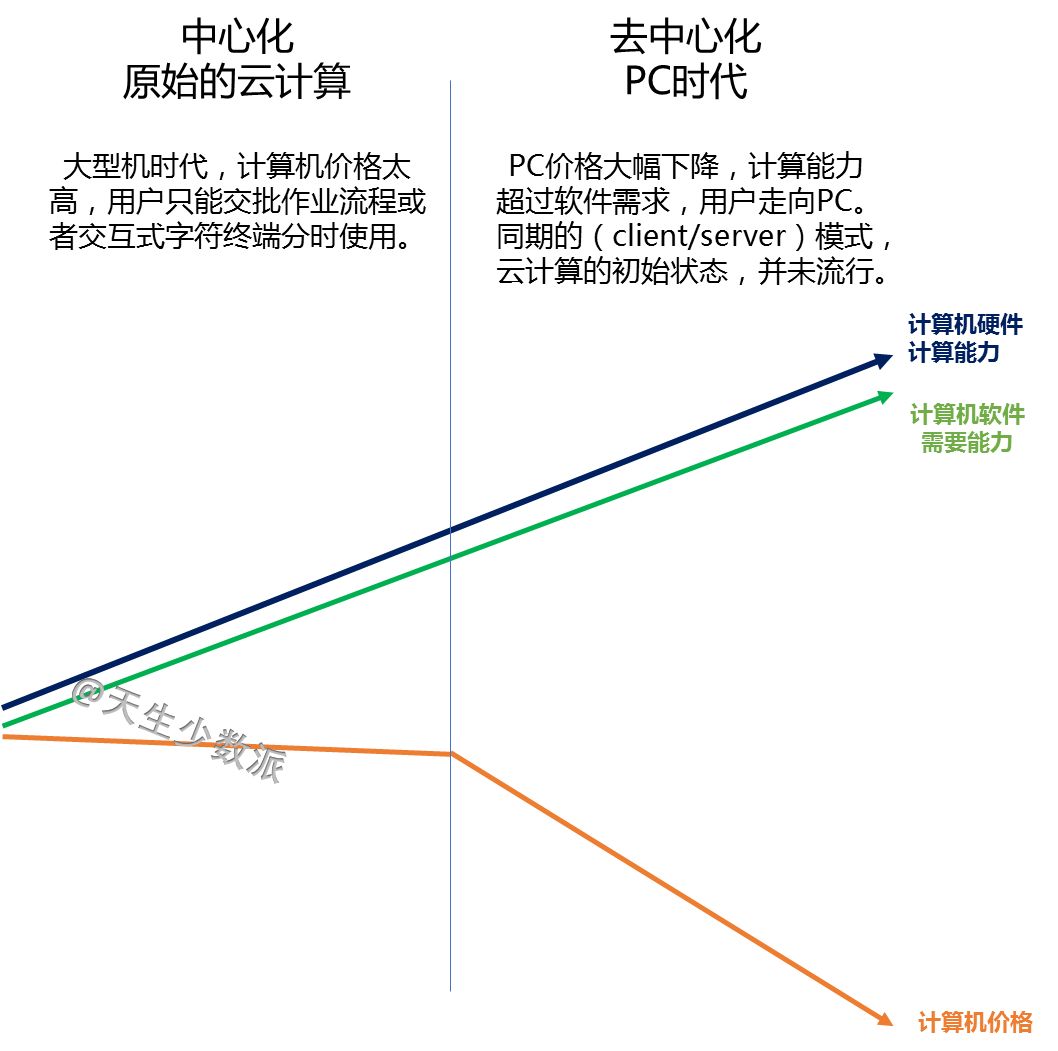
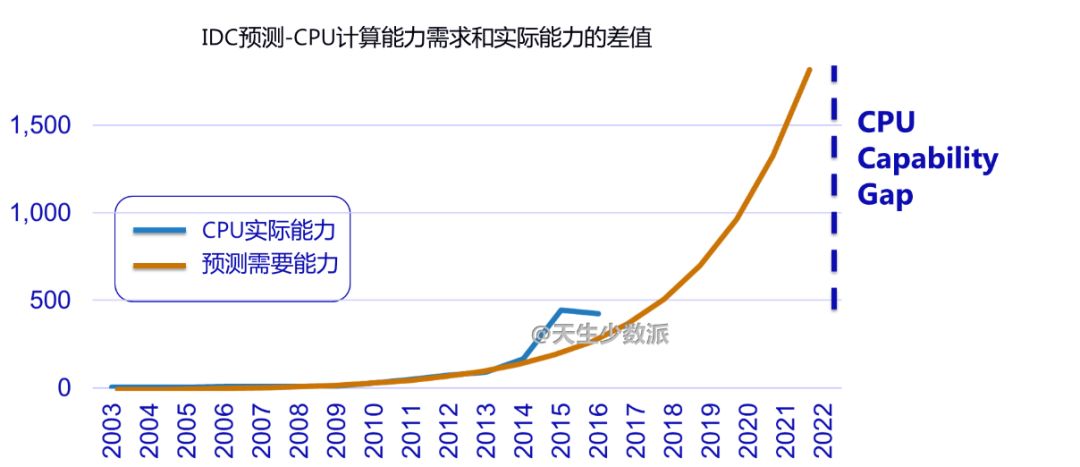
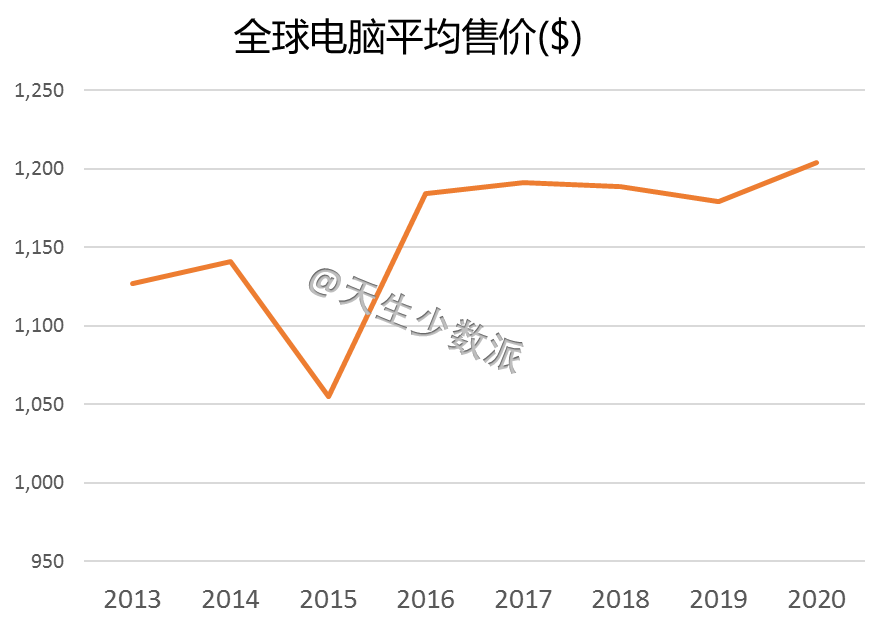
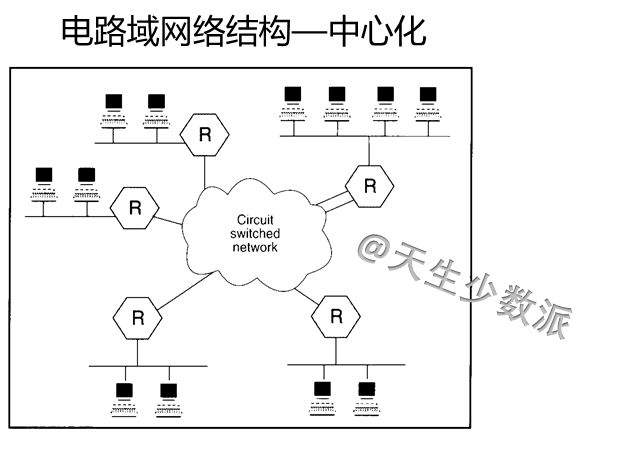
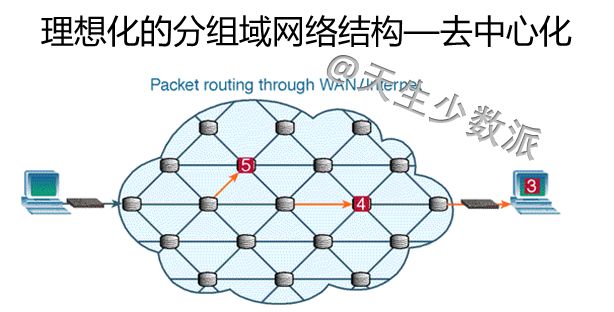
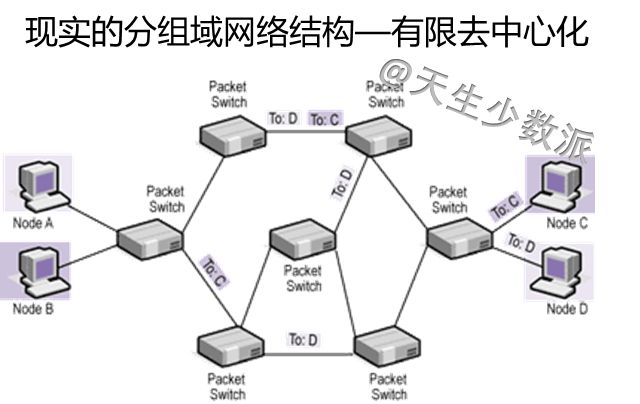
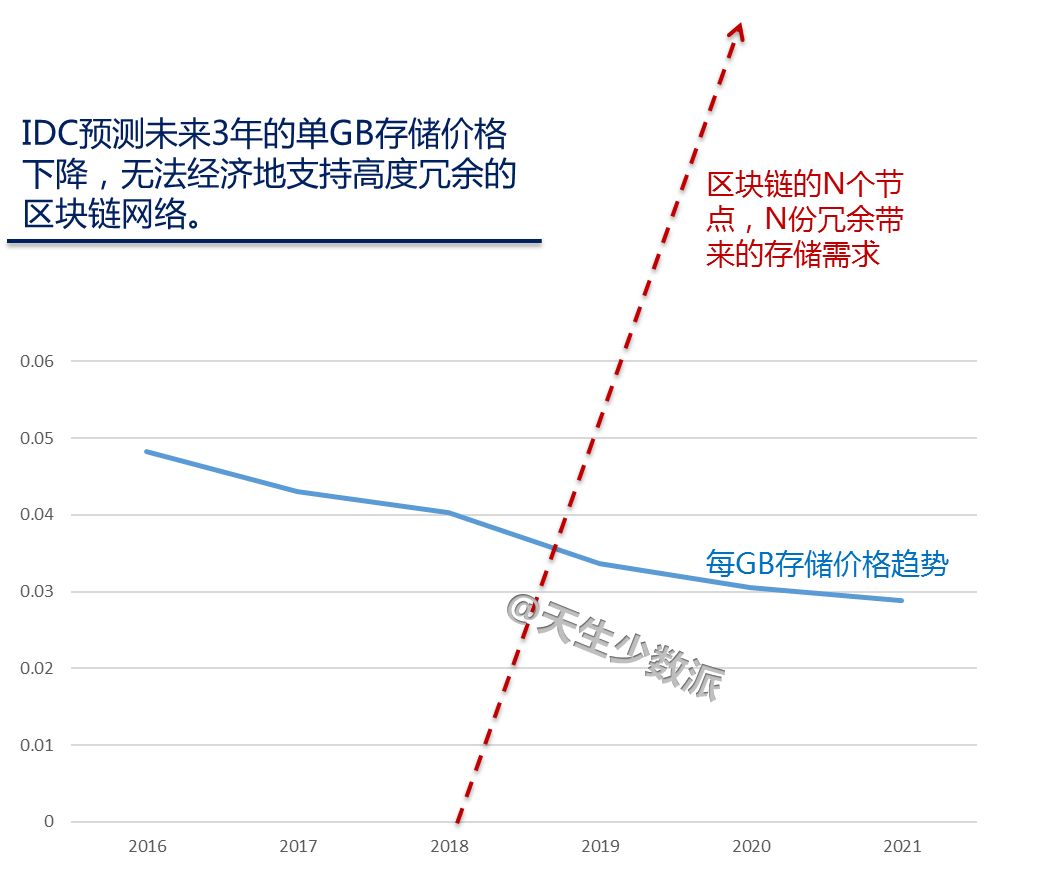
Before Facebook, because Cambridge analysts had stolen more than 50 million users' personal information, it affected the election of Brexit and President Trump of the United States, causing Zuckerberg to apologize directly. After that, companies such as Didi and Uber used big data to “killâ€. At one time, the privacy of personal privacy and the abuse of big data made the public begin to worry about the hegemony and ability of digital giants. Cloud computing, just beginning to grow rapidly, has been questioned. At the same time, the decentralization of the blockchain, known as "there is no centralized institution to control it, everyone knows what is happening," the new technology allows everyone to see complete "democracy and security" Hope. Will cloud computing decline? When will the utopia described by the blockchain come? 1. Blockchain to the left and cloud computing to the right Cloud computing is the product of the convergence of traditional computer and network technologies such as distributed computing, parallel computing, utility computing, network storage, virtualization, load balancing, and hot backup redundancy. Many cloud computing deployments rely on the tightly coupled work of computer clusters, but they differ greatly from grid computing, the architecture, purpose, and working methods of this loosely coupled approach. Cloud computing emphasizes that computer clusters work like a computer. In addition to providing computing services, cloud computing services must also provide storage services. "Cloud" is a huge resource pool that reduces redundancy and increases resource utilization, but reduces reliability. Regardless of the strengths of the cloud computing technology it provides, user data is unavoidably "stolen." Blockchain is a new application mode of computer technology such as distributed data storage, point-to-point transmission, consensus mechanism, and encryption algorithms. The chain structure of the blockchain, coupled with distributed accounting and consensus mechanisms, determines that data cannot be tampered with. Blockchain is a decentralized technology, emphasizing that there is no centralized organization to control it. Everyone knows what is happening. However, taking Bitcoin as an example, the blockchain system places too much emphasis on “going to the centerâ€, which in turn affects its efficiency, cost, and supervision. To achieve "decentralization", the Bitcoin blockchain system requires a large number of external computers to access and operate together (this is the basic condition for the "decentralized" operation). The more computer nodes that join, the more bitcoin mining and the The greater the difficulty of transfer, broadcast, verification, and distributed processing across the entire network, the higher the cost and the lower the efficiency. The original centralized storage method, once the central control institution itself or the centralization mechanism is hacked, can easily be modified, but now it is necessary to break at least half of the nodes or computing power of the entire network. Even if the attack succeeds, the participants will find that there is a problem with the chain, the entire chain is equivalent to abolished, the assets obtained by the hackers have no value, and the attack is not worth the damage. The distributed accounting of blockchain is to use high redundancy to ensure security. The disaster recovery solution generally provided by cloud computing vendors is "three centers in two places." Bitcoin and Ethereum have one copy for each node, totaling hundreds or thousands of copies, obviously not saving at all. The Utopia blueprint of the blockchain is a “beautiful world†of “decentralizationâ€, decentralization, democratic fairness, no human control and corruption, and security and stability. Imagine not using Uber or Drips, but rather a blockchain version of Uber or Drip, which is essentially a collaborative organization shared by its members. When potential passengers want to rent a car, the software will search all the car sources on the blockchain and filter the car sources that meet the passenger's requirements. Blockchain will not make taxi drivers unemployed, but will make Uber or drop unemployed and allow taxi drivers to serve customers directly. Blockchain, decentralized, uses redundancy to ensure high security. Cloud computing, centralized, with centralized reduction of redundancy to increase efficiency. Which way is the future? Will the utopia of the blockchain description be realized? 2. The long-term division must coincide The development of computer technology has experienced the evolution from the mainframe, personal computer, client/server computing model, to the rise of today's Internet computing model and cloud computing. It has undergone a process of centralization, decentralization and centralization. What is the economic driving force behind this? There is no doubt that for the end user, having autonomy on the computer is certainly best. But this "autonomy" is pricey. In the mainframe era, individual users cannot afford the cost of owning a computer. The original cloud computing and interactive terminal approach followed suit. With the substantial decline in PC prices, the actual computing power of the CPU is also higher than the software demand, and consumers are rapidly turning to the PC. In the late 1990s, salesforce pioneered the concept of providing remote services in enterprises. In 2002, Amazon enabled the AWS platform. In 2006, the emergence of the term cloud computing did not achieve rapid development. As can be seen from the figure below, an important factor is that demand is not strong. The computing power in PC mode is sufficient. Since 2015, the emergence of big data, machine learning and artificial intelligence has increased the demand for storage and computing power exponentially, and the actual capabilities of CPUs have not kept pace. Not only did the price of computers not fall, it also rose. The user's choice is simple. The cost of ownership of such a computer is too high, renting becomes a more economical choice, and cloud computing has become the first choice. "The long-term division must be combined, and long-term integration must be separated." Behind the changing trend of the computer is the wrestle of two major factors: the evolution of software algorithms to enhance the computing needs, whether hardware development can produce reasonable price calculation and storage capabilities. Finally, the end user decides whether he or she is willing to pay for having such computer autonomy. 3. Decentralization of ICT History Prior to the advent of TCP/IP, the basis for building a telecommunications network architecture was “circuit switching,†in which the connections between the two parties or machines must be established in advance and remain connected throughout the exchange. To ensure that any two nodes can communicate with each other, telecommunication service providers and equipment manufacturers have invested billions of dollars in establishing telecommunication lines. Any connection must go through a central node. TCP/IP overturns the circuit switching mode. The new protocol passes information by digitizing the information and breaking it into tiny groups, each containing address information. After the information of each group is sent to the network, it can take any path to reach the receiving end. Intelligent sending and receiving nodes at the edge of the network are able to split and reassemble each group of information while interpreting the encoded data. There is no need to build private lines or large-scale infrastructure. In theory, TCP/IP created an open source shared public network. No central organization is responsible for its maintenance and upgrades, as shown in the following figure. TCP/IP creates a "decentralized" network architecture with great redundancy. Of course, this connection is not economical. In reality, this ideal “decentralized†structure does not appear in the network. It still needs several central routing nodes to support the network. The central node is equipped with a disaster recovery backup. The cost of security created through redundancy is extremely high. After decades of evolution, the TCP/IP network has only finally achieved limited decentralization because the cost of idealized infinite redundancy is too high. If each node is equipped with a 100G PON, an ideal decentralized network is possible, but users choose to reduce security and reduce costs. 4. The Future of Blockchain and Cloud Computing Integration There is no doubt that blockchain technology can theoretically create a completely secure and democratic network. However, the price that users are willing to pay for “security†is limited, unless the prices of storage and CPU can be reduced indefinitely, and blockchain will be implemented first in some high-end areas, such as the financial industry; but the entire population and all areas of the Internet of Things will be realized. Block chaining can only be another utopian dream. Looking at the simplest application of the blockchain alone: ​​distributed accounting functions, each user has an additional storage of N-1 user data, there is no support for a substantial drop in storage prices, the "absolute security" of the cost of the account for ordinary users. Words, too high. From the history of replacing circuit domain networks with TCP/IP networks, it can be predicted that future blockchain and cloud computing will be fused inevitably, small nodes will be clouded, and important node blocks will be chained. Even with limited backup scenarios, each node's data does not have to be backed up on N-1 nodes, but only on 50% or even 30% of the nodes. Because "safe" has a price. There is no "absolute security" network, only the most economical and reasonable network. 2.1 Home Theater Speaker,2.1 Speaker System Home Theater,Surround Sound Speakers,2.1 Home Theater GUANGZHOU SOWANGNY ELECTRONIC CO.,LTD , https://www.jerry-power.com